A DC motor (direct current motor) has a lot of applications in today’s field of engineering and technology. From electric shavers to automobiles, DC motors are everywhere. As you may know, DC motors are divided into two categories depending upon whether or not they use brushes and commutators which are Brushless motor and Brushed motor. The right DC motor of either type can make a project far more efficient. Therefore, understanding the difference between brushless motor and brushed motor is of great importance. Follow this new article in Linquip to learn more about each and their main differences.
What Is a Brushless Motor?
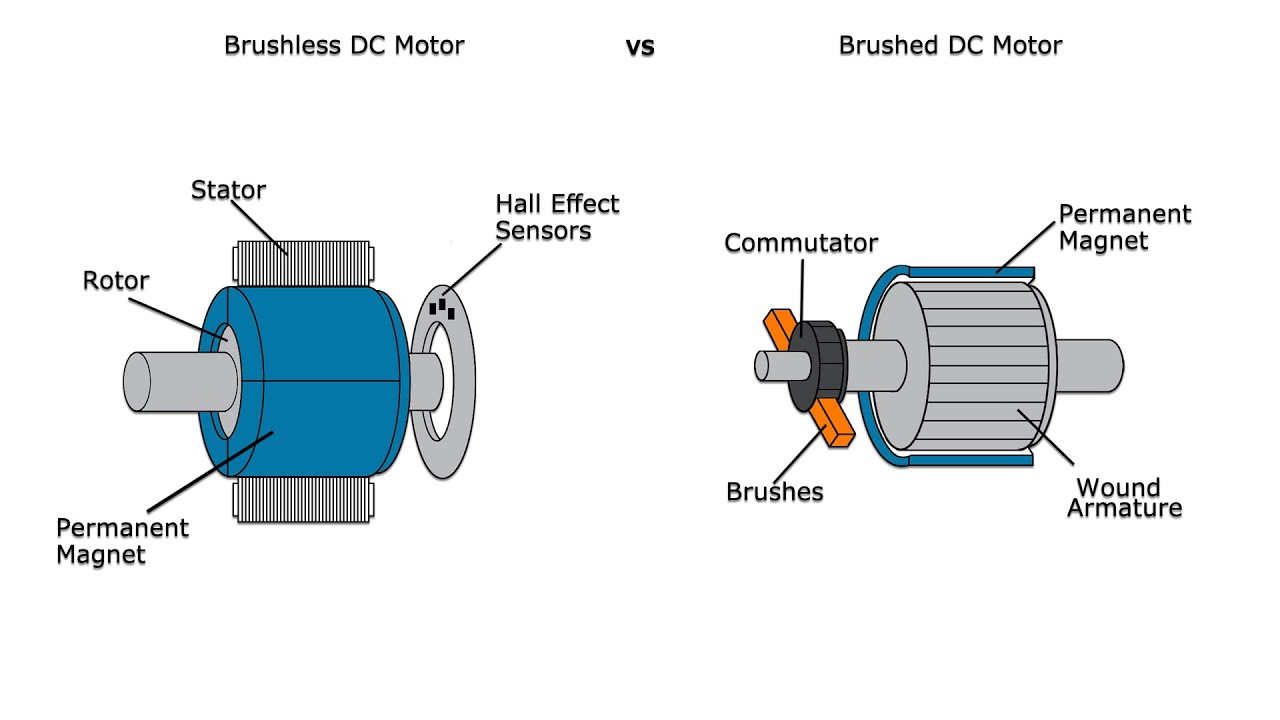
A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC motor), also known as the electronically commutated motor (ECM) are synchronous motors powered by direct current (DC) electricity via an inverter or switching power supply which produces electricity in the form of alternating current (AC) to drive each phase of the motor via a closed-loop controller.
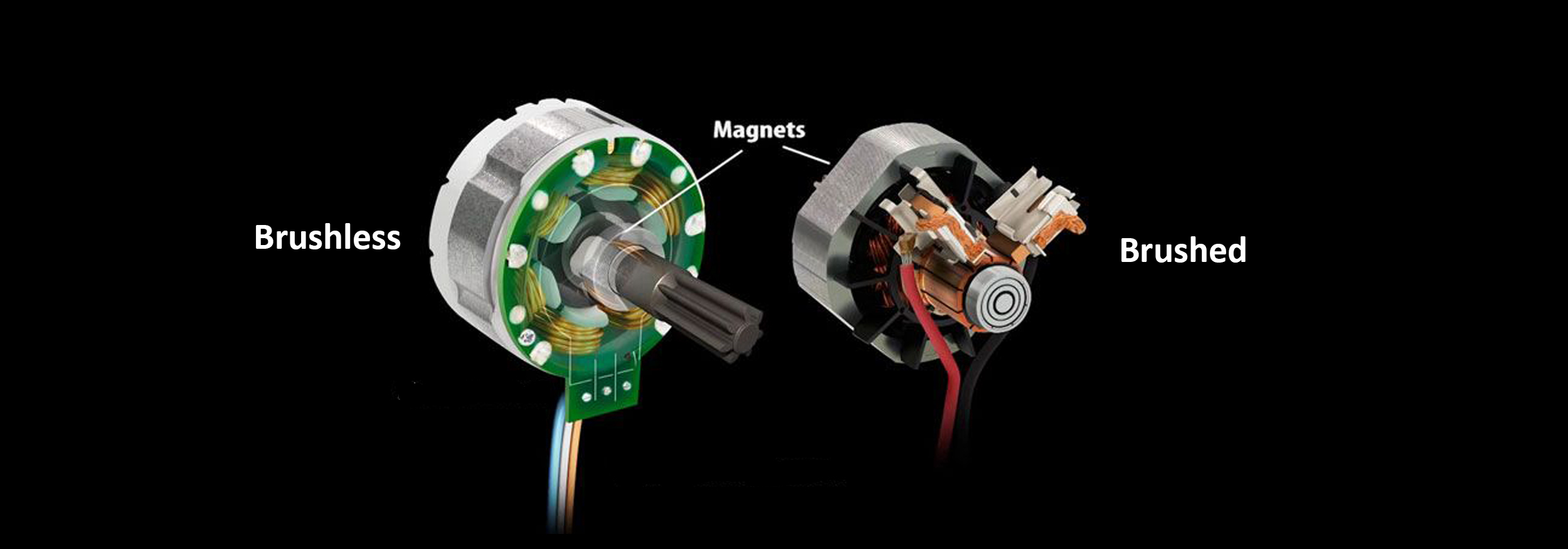
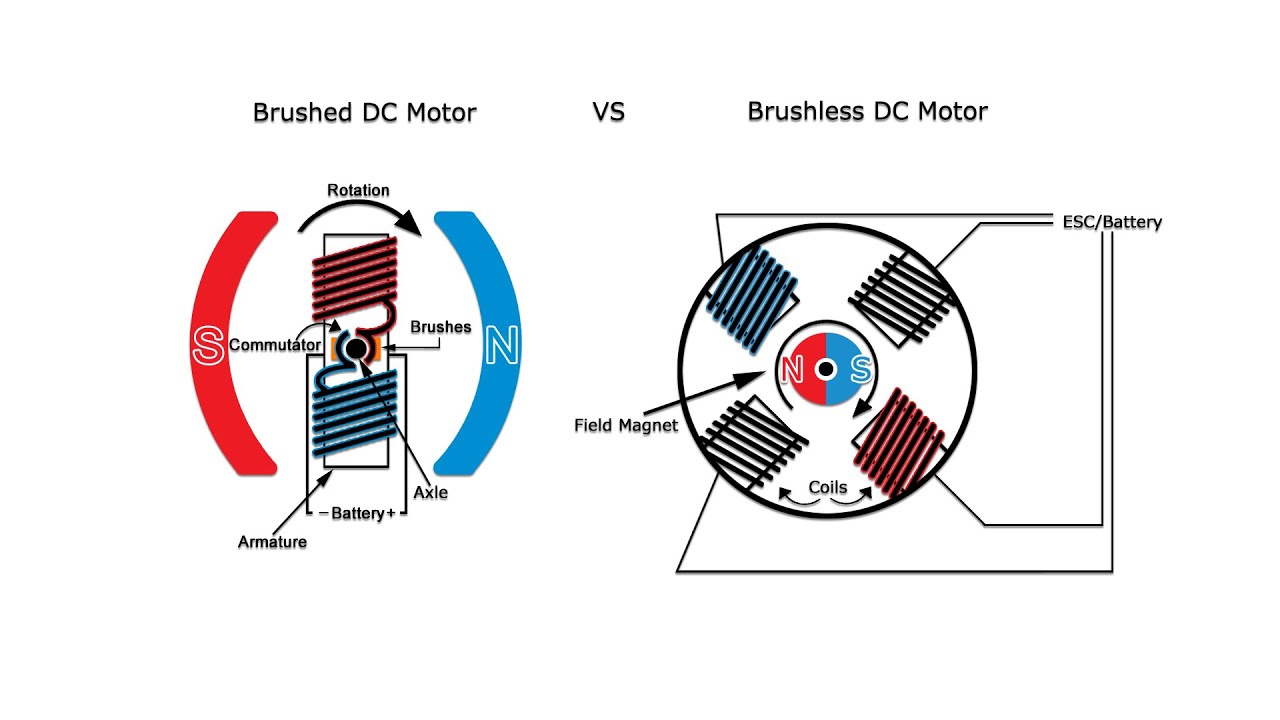
A brushless DC motor eliminates the need for brushes to flip the electromagnetic field. In brushless DC motors, the permanent magnets are on the rotor and the electromagnets are on the stator. A computer then charges the electromagnets in the stator to rotate the rotor a full 360-degrees.
What Is a Brushed Motor?
A brushed DC electric motor is an internally commutated electric motor designed to be run from a direct current power source. Brushed motors were the first commercially important application of electric power to driving mechanical energy, and DC distribution systems were used for more than 100 years to operate motors in commercial and industrial buildings.
In a brushed DC motor, the rotor spins 180-degrees when an electric current is run to the armature. To go any further, the poles of the electromagnet must flip. The brushes, as the rotor spins, make contact with the stator, flipping the magnetic field and allowing the rotor to spin a full 360-degrees.
The Difference Between Brushless Motor and Brushed Motor
As their names imply, the main difference between brushless motor and brushed motor is the use of brushes and commutators in brushed motors while brushless motors use electrical commutation to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Several factors are taken into account when comparing brushless and brushed motors which are as follows.
-
Commutation
Brushed DC motors use brushes to deliver current to the motor windings through mechanical commutation while brushless motors use Electrical commutation to deliver the current.
-
Speed Range
The speed range in brushless motors is higher than brushed types due to the absence of brushes and commutators.
-
Electrical noise
Brushless motors make less noise than brushed ones. This is because electrical noise, in particular, is the result of the strong sparks that tend to occur in the areas where the brushes pass over the gaps in the commutator. This is why BLDC motors are often considered preferable in applications where it is important to avoid electrical noise.
-
Speed Control
Brushless motors offer higher speed controllability compared to the brushed types. They can be controlled, using feedback mechanisms, to deliver the desired torque and rotation speed precisely. Precision control in turn reduces energy consumption and heat generation, and in cases where motors are battery-powered lengthens the battery life. While brushed motors require more complicated methods of speed control. Lowering voltage reduces the motor’s torque, but this comes at a cost of lower speeds as torque drops off dramatically.
-
Efficiency
Brushless motors can be controlled continuously at maximum rotational torque. Brushed motors, in contrast, reach maximum torque at only certain points in the rotation. For a brushed motor to deliver the same torque as a brushless model, it would need to use larger magnets. This is why even small BLDC motors can deliver considerable power.
Besides, due to power losses through friction and power transfer via its commutator system, brushed motors are relatively inefficient. Brushless motors, on the other hand, are more efficient due to the lack of mechanical losses seen in brushed motors.
-
Life Span
Owing to their design, brushed motors have shorter lifespans, due to the wear and tear of the brushes. Typically they require replacement every two to seven years, depending on operating temperatures and working environment.
-
Maintenance
As brushless motors lack brushes and physical commutators, they require less overall maintenance than the brushed types.
-
Speed/torque characteristics
Brushed motors tend to run too fast to be useful for most applications. For this reason, they tend to require a gearing system to reduce the speed and thereby increase torque. Brushless motors, however, excel in this regard. For this reason, they are frequently used directly without the need for gearing. Some specialist applications may employ gearing if they require very high precision or more torque.
-
Safety
Brushed motors can generate sparks, which is not ideal in places where there is a risk of explosion. For this reason, brushless motors are often the preferred choice in hazardous working conditions.
-
Electrical consumption
Many tools that use brushless motors are often called “smart motors”. This is because sensors are used to determine the resistance against the motor for things like electric drills. The current supply can therefore be automatically adjusted. This allows such tools to be very efficient from an electrical consumption point of view.
-
Cost
Given the relative complexity and presence of permanent magnets in brushless motors, it will come as no surprise that they tend to be more expensive. Brushed motors, on the other hand, are relatively cheap.
-
Construction
In brushed motors armature winding is on the rotor; Fixed magnets are placed on either side of the rotating electromagnet. While in brushless motors, armature winding is on the stator and fixed magnets are on the rotor.
-
Applications
Brushed motors are used in home appliances, kid toys, industrial applications, medical equipment, robots, and drones to electric cars, power tools, etc. Brushless motors are used in electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and electric bicycles, industrial applications, drones, washing machines, fans, pumps, and blowers, etc.
That was everything you needed to know about the difference between brushless motor and brushed motor. As you see, higher efficiency, lower electric noise generation, being faster, etc. have made brushless motors a better choice compared to the brushed ones. Comment below and let us know what you think about these two and their differences. And if you have any questions about gas turbines or reciprocating engines, feel free to sign up on Linquip and we will help you right away!