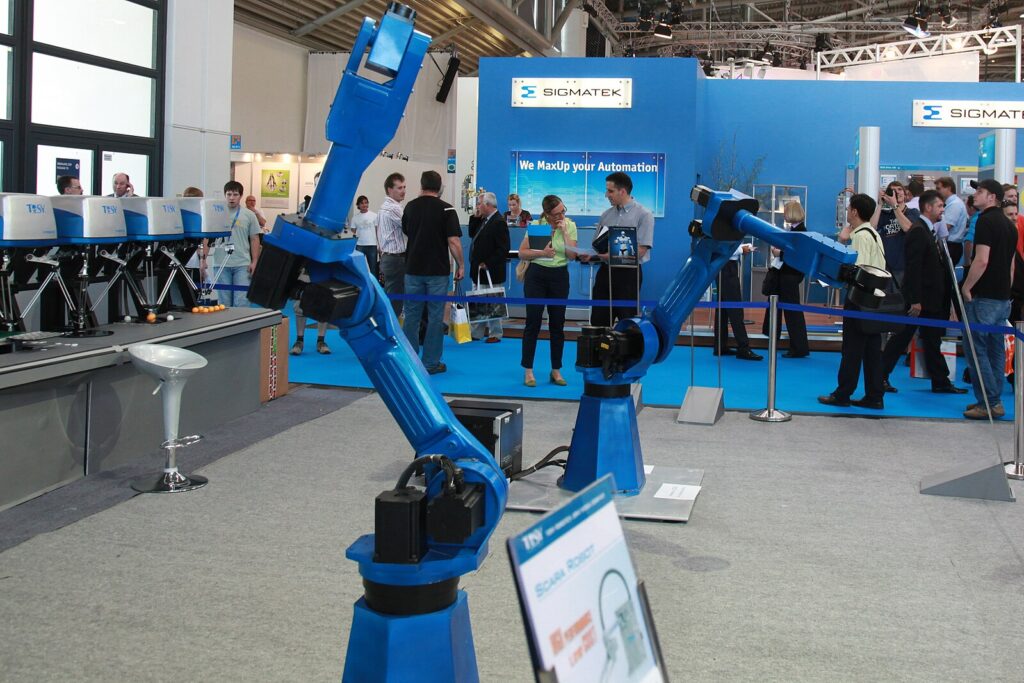
Automation refers to the use of technology to make repetitive tasks run independently without human input or with very little of it. Perhaps the most well-versed form of automation is the use of robotics in production lines. But there are other forms of automation for manufacturing and assembly, which are critical because they provide these benefits.
Benefits of Automation in Industrial Settings
Lower Operating Costs
Automated machines like robots can perform the work of 3–5 workers while running at full speed. In a car production line, for instance, a robotic welder can weld two or even three spots at the same time, and it can do this independently or with the assistance of one worker, instead of three. As such, the factory won’t need as many personnel, which leads to reduced operating costs.
Improved Worker Safety
Robots can handle tasks that expose human workers to hazards, such as toxic fumes, high temperatures, fires, and falling objects.
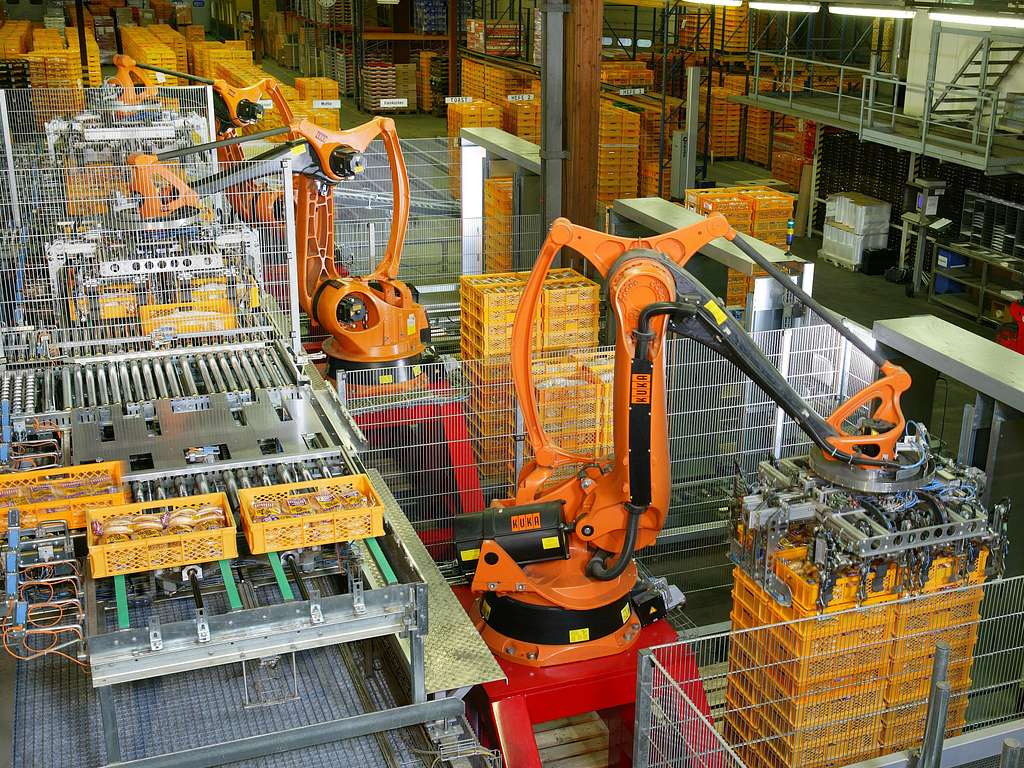

Industrial robots palletizing bread
Better Product Quality
Besides efficiency, automation eliminates the human error aspect during production, leading to better product quality.
Faster ROI
Machines run 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The only downtime is during repairs, which is not often. In the long run, automated machinery increases production output and product quality, resulting in higher profits and more competitiveness in the market. These lead to a faster ROI.
What Is Needed To Enable Automation
Automation is basically like several humans working full-time, but on steroids and without getting tired. This mechanism needs feedback to optimize and adjust operations for maximum efficiency. It also needs to control the various aspects of the manufacturing process, such as closing valves, switching, and moving parts.
So the central part of the system is a control panel, which can be PLCs, I/O modules, or HMIs. Typical peripherals are valves, pumps, actuators, compressors, and heat exchangers for control. On the other side are the data-gathering devices or sensors, which include thermostats, flow sensors, cameras, pressure, and torque sensors, among many others.
All these components need wiring harnesses to transmit control signals and data between them, and the most commonly used ones are Molex cable assemblies. Cables with Molex connectors provide secure and durable connections in harsh environments while providing high-power and high-speed data transmission. Additionally, they can be customized to meet different application needs.
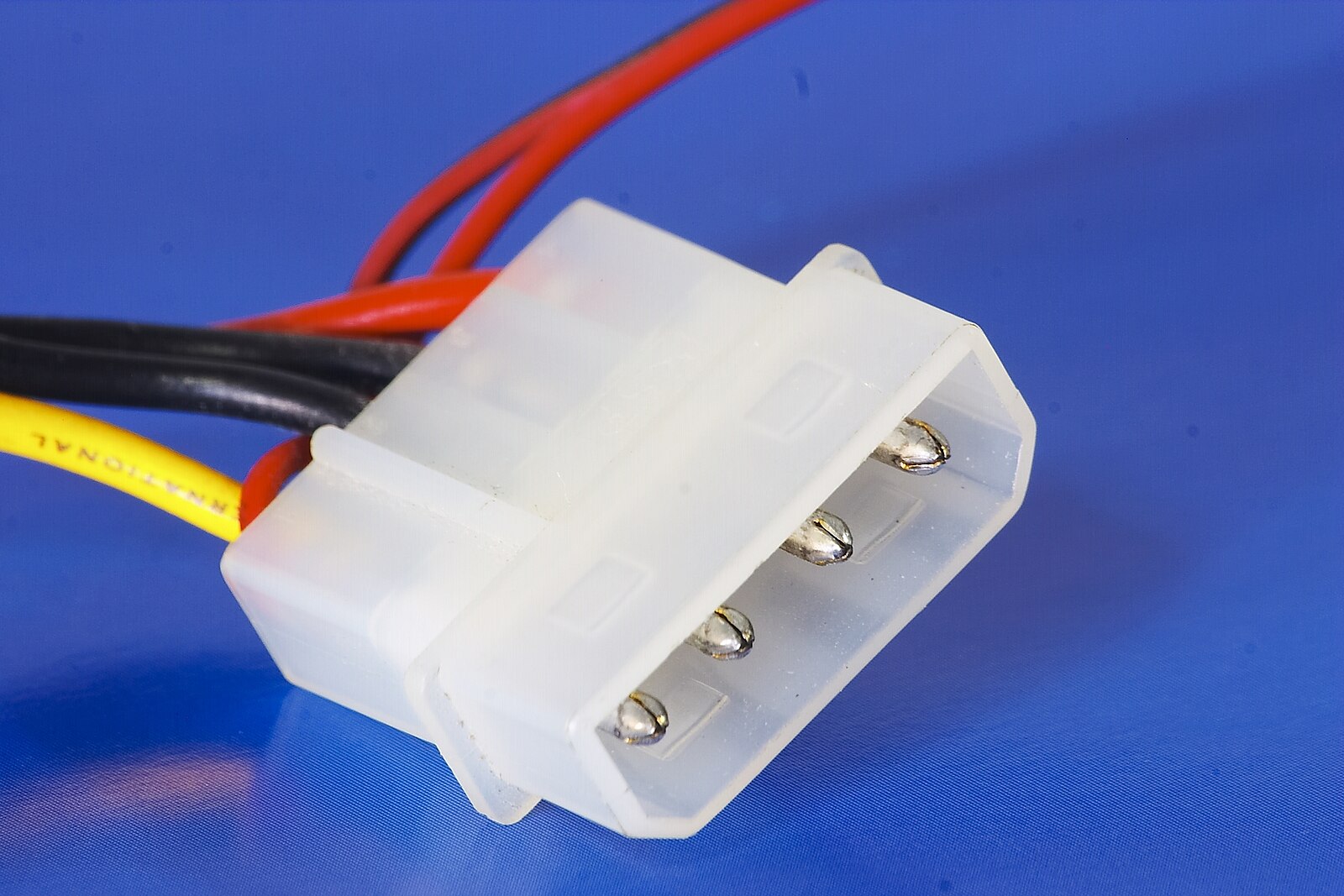
A male Molex connector
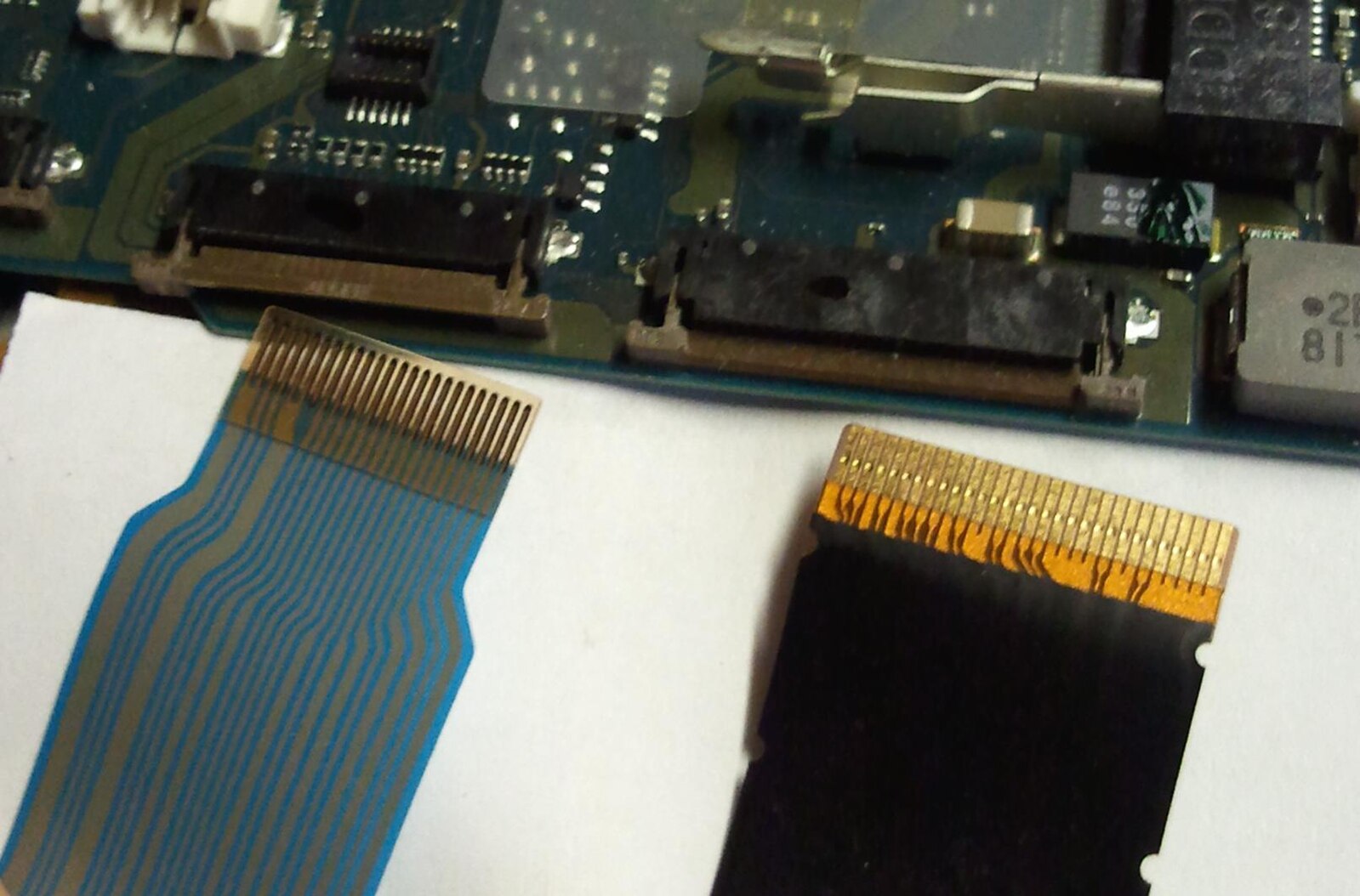
Since the setup has at least one PCB and LCD, you’ll also need FFC cable assemblies to connect PCBs to displays or boards to boards. Flexible flat cable assemblies are thin, flat, ribbon-like wire harnesses that are designed to fit in tight spaces.
Why Choose Wiringo As Your Industrial Automation Equipment Manufacturing Partner
Wiringo is an industry leader in providing custom wiring harness solutions for different applications, and it specializes in manufacturing Molex and FFC cable assemblies for industrial automation.
The company’s Molex custom cable assembly options include:
- High-power cable assemblies
- Sealed cable assemblies
- Discrete wire cable assemblies
- Multi-branch wire harnesses
- Overmolded cable assemblies
- Ribbon cable assemblies
Their FFC cable options are also diverse and include:
- FFC cables with IDC connectors
- FFC wires with discrete wire connectors
- FFC cables crimped with receptacle housing
- Overmolded FFC cables
- ZIF-style FFC cable assemblies
- FFC cables with latching receptacle housings
Two FFC cable assemblies for ZIF-style connectors
The company’s strength lies in customization, so their industrial automation cable assembly manufacturing and assembly options are not limited to the ones listed above. Contact them with your specifications or OEM wire harness designs for precise and high-quality replication at reasonable costs.