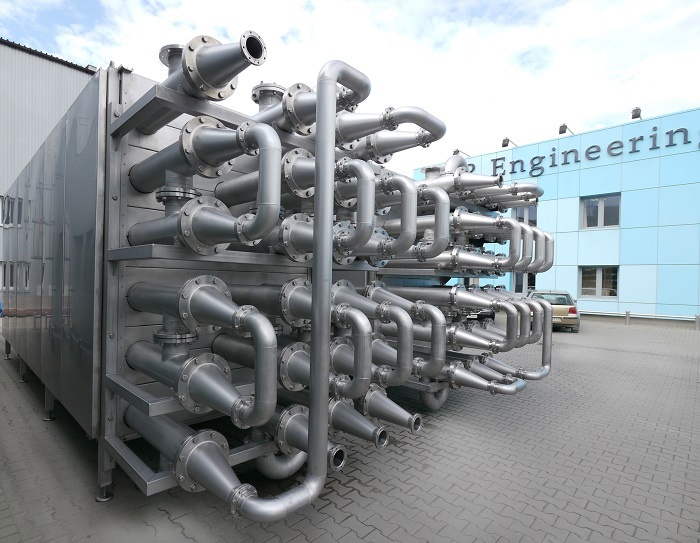
Welcome to Linquip Blog. Today and in this article, we are going to deal with Tubular Heat Exchangers. The information in this article gives a significant collection of data you need to know about the structure, working principle, applications, and privileges of Tubular Heat Exchangers. A tubular heat exchanger is one of the heat exchangers, a device used to transfer or exchange heat or thermal energy with the help of flat tube series.
Our team gathered all of the necessary information on this topic to eliminate the need for reading diverse content on other websites. Stay with us until the end to find the answer to your question on this topic.
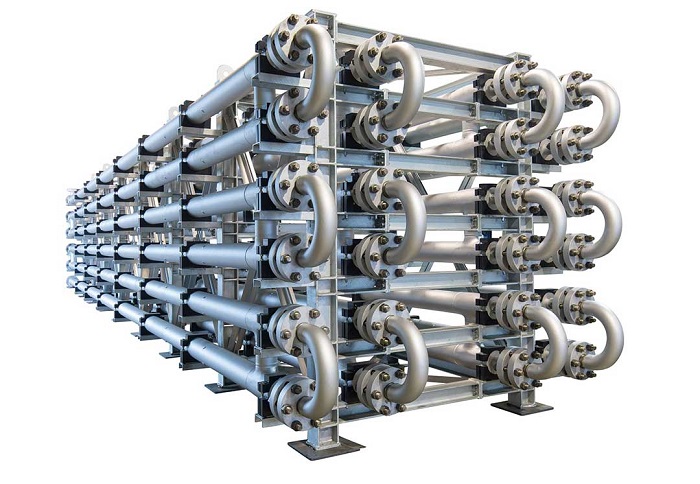
An Introduction to the Tubular Heat Exchanger
The Flat Tube Heat Exchanger is an air-to-air heat exchanger operating on the principle of forced draught convection. Process gases pass over the outside surfaces of the heat exchanger elements. Cooling air is generated from ambient air by axial or centrifugal fans and blown along with the bores of the heat exchanger elements thus promoting the exchange of heat.
Dependent on dust characteristics and quantities the Heat Exchanger can be equipped with a cleaning device. This cleaning device ‘wipes’ the surfaces of the heat exchanger elements and removes excessive dust, thus maintaining the efficiency of the heat exchanger.
The Flat Tube Heat Exchanger can be used to cool process gases down to a suitable operating temperature for the selected filter media. The normal maximum inlet temperature for the Heat Exchanger is 550 deg. C.
How Does a Tubular Heat Exchanger Work?
In pharmaceutical applications, the risk of mixing between the product and the heating or cooling medium is eliminated thanks to a double tube sheet design. The product flows in the tubes while the service fluid flows around the tubes inside the shell. Service fluid is sealed in the shell by one tube sheet and a second tube sheet seals the product.
Heat exchangers with double tube sheets make leaks easy to spot because they appear at the joint in the outer tube plate. The heating fluid is sealed in the shell by the first tube sheet and the second tube sheet seals the product. In the event of a leak, the leakage of either fluid is easily visually detected.
Shell and tube heat exchangers are especially effective in the pharmaceutical industry where product hygiene and demand for isolating products from heating/cooling fluids are especially high. To meet the industry’s demands, high-quality tubular heat exchangers control microbe growth and prevent cross-contamination.
Some of the newest tube-in-tube designs for pharmaceutical applications feature high shear force and turbulence to maintain the efficient transfer of heat while reducing bio-film.
Smaller, lighter-weight heat exchangers designed for tighter spaces can be effective substitutes for larger tube heat exchangers. They feature the same hot and cold fluid flows through alternating channels that create high turbulence for high heat transfer efficiency while using 50–80% less heat transfer area.
Applications of a Tubular Heat Exchanger
The tubular heat exchanger is a process equipment used in different industries, and its applications are very diverse and varied. The advantages of tubular heat exchangers make them very robust, reliable, and low-maintenance equipment, due to the absence of joints.
Within the main applications of tubular heat exchangers, we highlight the following applications:
1. Sanitary applications: Applications destined for the Food Industry with optimized designs to favor a good CIP cleaning (Clean in Place) of the product channel, guaranteeing the best finishes and trainability.
2. Pharmaceutical applications: Applications destined for the Pharmaceutical Industry, in which the roughness certification plays a key role, and whose design is specially designed to avoid cross-contamination
3. Industrial applications: Applications destined for the Chemical and Petrochemical Industry (Oil and Gas), whereby high priority has been given to ensure long life and high reliability.
Advantages of Tubular Heat Exchangers
Within the different geometries of heat exchangers present in the market as plate and gaskets, welded plates, and spiral or scraped surface heat exchangers, among others, tubular geometry is one of the most traditionally used.
The main advantages of tubular heat exchangers are as follows:
- Low maintenance cost
- High working pressure
- High working temperature
- Processing of particulate
- Easy inspection and disassembly
- High security in aseptic processes
- Easy to enlarge
Conclusion
The present article was an attempt to deal with Tubular Heat Exchangers and deliver all the essential information about how they work and where they are used. A Tubular heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger, a device used to transfer or exchange heat or thermal energy with the help of flat tubes.
If you have any experience of using Tubular Heat Exchangers, we will be very glad to have your opinions about their performance in the comments on our website Linquip. Moreover, if you have any questions about this topic, you can sign up on our website and wait for our experts to answer your questions. Hope you enjoyed reading this article.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip





Will tubular heat exchanger run with freon gas?