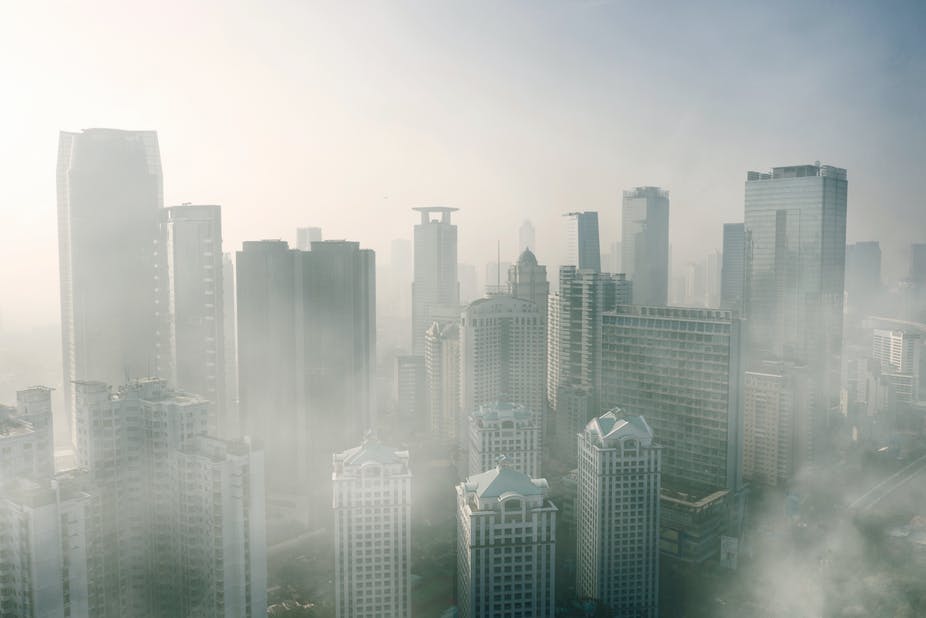
Air pollution points to the discharge of pollutants into the air that is detrimental to humans’ health and other living beings or causes damage to the materials or climate. There are several types of air pollutants, including gases (such as carbon monoxide, ammonia, nitrous oxides, sulfur dioxide, methane, and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both inorganic and organic), and biological molecules. Air pollution may provoke allergies, diseases, and even death to people; it may also harm other living organisms, namely food crops, and animals, and may harm the natural environment (e.g., habitat degradation, climate change, or ozone deficiency) or built environment (e.g., acid rain). Both human activity and biological processes can cause air pollution.

What is Air Pollution?
As mentioned before, air pollution attributes to the discharge of pollutants into the air that is harmful to social health and the planet as a whole.
Air pollution is a notable risk factor for several pollution-related diseases, including heart disease, respiratory infections, COPD, lung cancer, and stroke. The human health influences of feeble air quality are far-reaching but substantially influence the body’s cardiovascular system and respiratory systems. Personal reactions to air pollutants depend on the variety of contaminants a person is exposed to, the level of exposure, and their health situation and heredity.
Indoor air pollution and inadequate residential air quality are listed as two of the world’s most dangerous toxic pollution difficulties in the 2008 Blacksmith Institute World’s Worst Polluted Areas report. Outdoor air pollution alone creates 2.1 to 4.21 million losses annually. By and large, air pollution causes the deaths of around 7 million people globally each year and is the world’s most considerable single environmental health hazard.
Productivity declines and depraved quality of life affected by air pollution are assessed to cost the world market $5 trillion per year. Different pollution restriction technologies and approaches are available to diminish air pollution. To reduce air pollution impacts, both national and international regulations and legislation have been performed to control air pollution. Local laws that were well supported in cities have led to substantial public health advances.
Some of these efforts have been flourishing at the international level, for example, the Montreal Protocol, which strongly reduces the release of harmful ozone-consuming chemicals, or the 1985 Helsinki Protocol, which decreased sulfur emissions, while other efforts have been less prompt in implementation, such as international action on climate change.
The Clean Air Act allows the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to preserve public health by controlling the discharges of these toxic air pollutants. The NRDC has been a foremost authority on this law since it was organized in 1970.
What Causes Air Pollution?
By definition, pollution applies to any matter that is “out of place”. To put it another way, it is what occurs when contaminants, toxins, and other unhealthy products have entered an environment, disturbing its natural functions and patterns. When it proceeds to our atmosphere, pollution points to the entrance of particulates, chemicals, and biological elements that can be detrimental to humans, plants, and animals and create damage to the natural environment.
Whereas some reasons for pollution are solely natural – being the outcome of unexpected changes in temperature, seasonal fluctuations, or natural cycles – others result from human impact (i.e. anthropogenic, or human-made). More and more, the consequences of air pollution on our planet, particularly those that result from human action, are of prominent concern to planners, developers, and environmental organizations, given the long-term influence they can have.
The atmosphere of the Earth, by composition, is made up of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and other trace gases (e.g. carbon dioxide and argon). This stability is vital to all life here on Earth, so the introduction of pollutants can have a severe damaging effect. On the whole, pollution can take various forms, like carbon compounds such as carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, sulfuric compounds like sulfur dioxide, radioactive decay, methane, or poisonous chemicals.
Besides, air pollution can be classified into Primary and Secondary classes of pollutants. Whereas primary sources create primary pollutants, i.e. the direct consequence of processes (such as volcanic eruptions or industrial emissions), secondary pollutants are the outcomes of intermingling and reactions by primary pollutants (such as water vapor and carbon emissions, which forms smog).

In what follows, we are going to describe some prominent causes of air pollution.
Natural Causes
Natural sorts of pollution are those that emerge from naturally occurring happenings. This indicates they are produced by regular activities that are not human-made or the result of human action. What’s more, these pollution sources are subjected to natural cycles, being more prevalent under specific conditions and less prevalent under others. Being part of Earth’s natural climatic fluctuations also suggests that they are sustainable over long periods. We will describe more details on the various types of natural causes of air pollution.
Dust and Wildfires
In vast areas of open land with little to no plants and are especially dry due to a lack of rainfall, wind can readily create dust storms. When added to the air, this particulate element can have a natural warming impact and can also be a health hazard for living animals. When scattered into areas with natural vegetation, particulate matter can also be a natural obstacle to photosynthesis.
Wildfire is a natural phenomenon in wooded regions when extended dry periods occur, generally due to season shifts and a lack of rainfall. The smoke and carbon monoxide produced by these fires contribute to the atmosphere’s carbon levels, which allows for more significant warming by making a Greenhouse Effect.
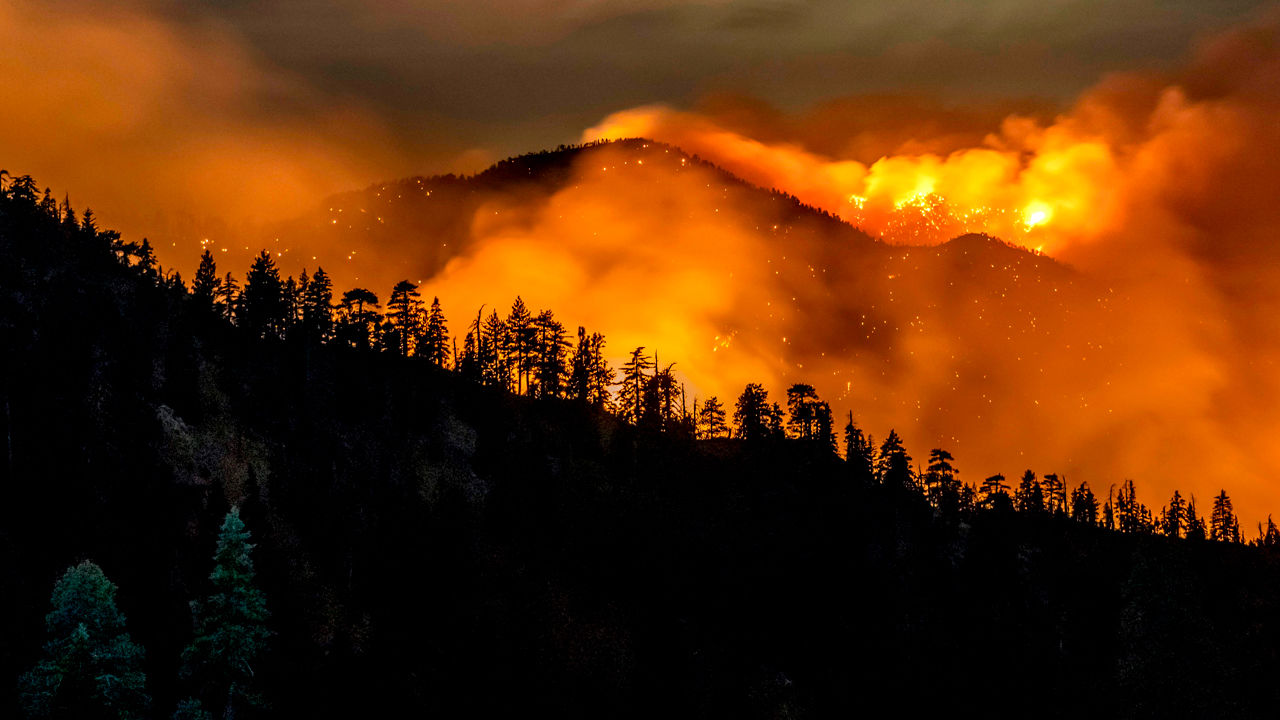

Volcanic Activity
Volcanic eruptions are a significant source of natural air pollution. When an outburst happens, it generates large amounts of chlorine, sulfuric, and ash products discharged into the atmosphere and can be lifted by winds to be scattered over vast areas. Additionally, compounds like volcanic ash and sulfur dioxide have been identified to have a natural cooling effect due to their capability to speculate solar radiation.
Animal and Vegetation
Animal digestion (especially by cattle) is another cause of natural air pollution, leading to the release of methane, another greenhouse gas. In some world areas, vegetation, such as poplar, black gum, willow trees, and oak, releases significant volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on hotter days. These act with primary anthropogenic pollutants, specifically carbon compounds, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide, to create low-lying seasonal hazes rich in ozone.
Anthropogenic Causes
But by far, the most numerous contributing to air pollution nowadays are those that are a consequence of human impact, i.e. human-made causes. These are primarily the result of human dependence on fossil fuels and heavy industry but can also be due to the collection of waste, automated agriculture, and other human-made manners. Here, there are some major varieties of Anthropogenic Causes of air pollution.
Fossil-Fuel Emissions
The combustion of fossil fuels such as natural gas, coal, petroleum, and other industry combustibles is a significant cause of air pollution. These are commonly used in power plants, manufacturing factories, and waste incinerators, as well as boilers and other types of fuel-burning heating appliances. Providing air conditioning and other services also needs meaningful amounts of electricity, leading to more emissions.
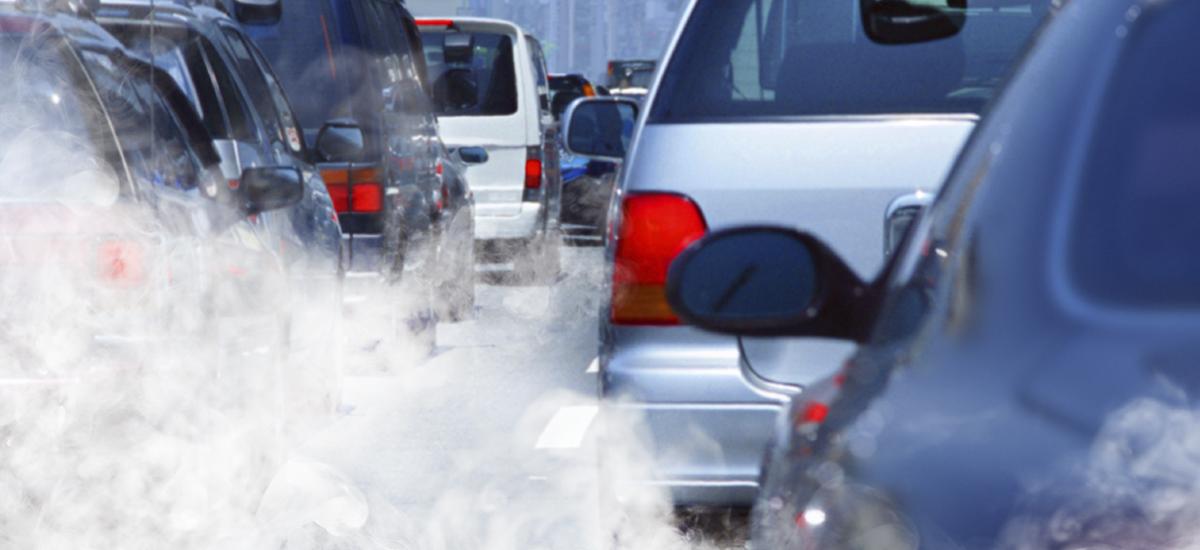
According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, manufacturing estimates for 21% of greenhouse gas discharges in the US, while electricity production is considered another 31%. Meanwhile, emissions created by gasoline-burning vehicles, i.e. carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, water vapor, and particulates, are also notable source of air pollution.
A study managed by the UCS in 2013 revealed that transportation estimated for more than half of the nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide and nearly a quarter of the hydrocarbons released into the air in the US. Globally, the condition is similar, with insignificant variations according to the sector. According to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report in 2014, industry accounted for 21% of cumulative greenhouse gas emissions, electricity and heat generation for another 25%, and transportation estimated for 14%.

Dissipation
Landfills are also identified to produce methane, significant greenhouse gas, and an asphyxiant and extremely flammable, likely dangerous landfill if landfills grow unchecked. Population extension and urbanization have a proportional connection with the production of waste, which leads to higher requests for dumping grounds that are far detached from urban environments. These areas thus became an important source of methane creation.
For some time, environmental scientists have been informed that the Earth has various self-regulating mechanisms. When it comes to the atmosphere of Earth, these mechanisms provide the sequestration of carbon and other pollutants, securing that the balance of its ecosystem prevails unchanged. Regrettably, the growing impact humanity has had on the planet is threatening to alter that balance permanently.
Fundamentally, we are supplementing pollutants to the air as well as land masses, and the oceans faster than the Earth’s natural mechanisms can eliminate them. Hence, the consequences of this are being felt in terms of acid rain, smog, global warming, and several health problems that can be directly associated with exposure to these harmful pollutants. If we plan to live on planet Earth, then sustainability and less pollution require to be our goals!
Animal Husbandry and Agriculture
A combination of factors produces greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture (the cultivation of crops and livestock); one is methane production by cattle. Another reason is deforestation, where the requirement for growing and pastureland fields needs to eliminate trees that would otherwise isolate carbon and clean the air.
According to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, agriculture estimates 24% of annual emissions. Nevertheless, this estimate does not incorporate the CO2 that ecosystems discharge from the atmosphere by sequestering carbon in biomass, soils, and dead organic matter, which offset around 20% of emissions from this sector.
Air Pollution Effects
Air pollution causes so many harmful effects on the environment and human health, which we will describe in what follows.
Respiratory and Heart Problems
The impacts of air pollution are dangerous. They are understood to produce various respiratory and heart diseases like emphysema, asthma, chronic bronchitis, strokes, and heart attacks, along with cancer, among other health threats. Numerous people are known to have died due to the direct or indirect influences of Air pollution.
Global Warming
Another direct impact is the quick alterations, designated as global warming, that the world is observing. With progressed temperatures worldwide, an increment in sea levels and ice melting from colder areas and icebergs, displacement, and habitat loss have already warned a coming disaster if efforts for protection and normalization aren’t undertaken quickly.
Child Health Problems
Air pollution is harmful to our health even before we take our first inhalation. Exposure to high air pollution levels during pregnancy creates miscarriages as well as premature birth, asthma, autism, and spectrum sickness in young kids.
It also has the potential to harm early brain advancement in a child and cause pneumonia that kills almost a million kids under five years. Children are at a more elevated risk of short-term respiratory diseases and pulmonary disorders in areas exposed to air pollutants.

Acid Rain
Harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides are discharged into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels. When it rains, the water droplets mix with these air contaminants, become acidic and then drop on the surface of the earth in the form of acid rain. Acid rain can cause significant harm to humans, crops, and animals.
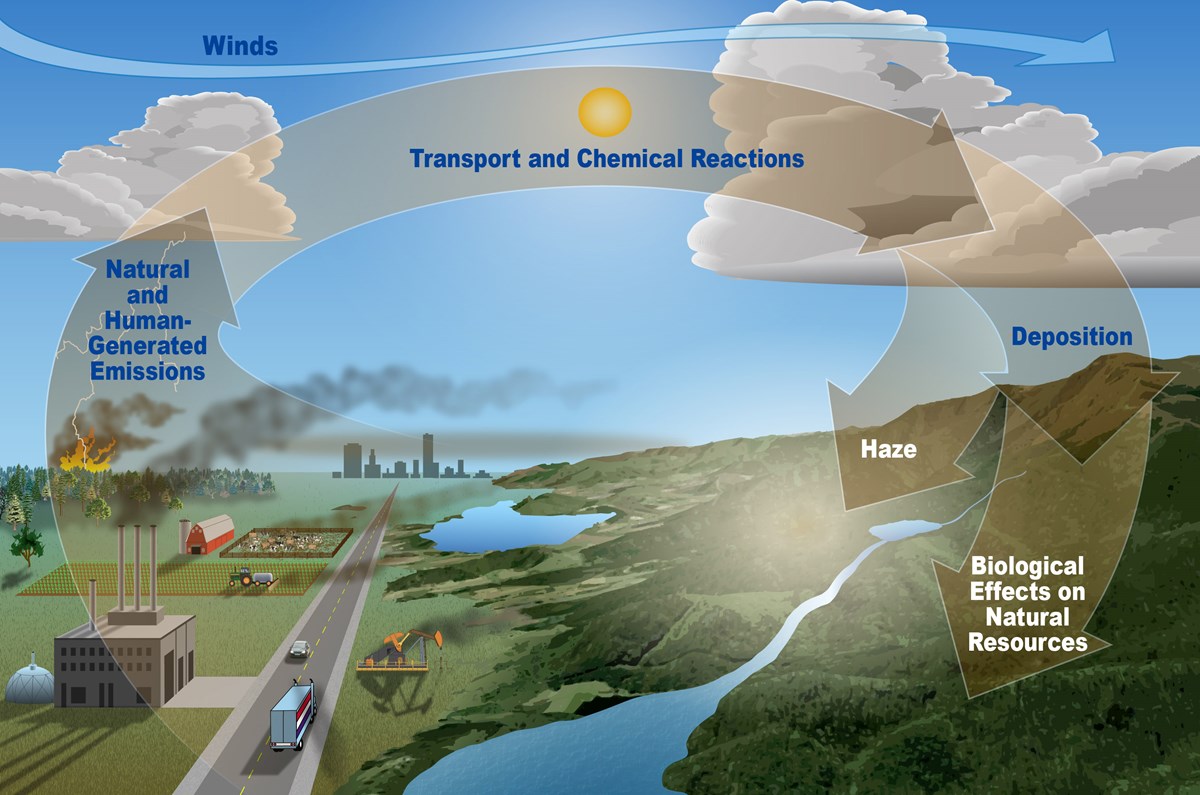
Effect on Wildlife
Just similar to humans, animals also suffer from the destructive consequences of air pollution. Toxic chemicals existing in the air can push wildlife species to travel to a new place and alter their habitat. The harmful pollutants deposited over the water’s surface can also influence sea animals.
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a situation where a large amount of nitrogen existing in some pollutants gets developed on the surface of the sea and converts itself into algae and negatively influences fish, animal species, and even plants.
The green-colored algae present in ponds and lakes are due to the presence of this chemical solely.
Depletion of the Ozone Layer
Ozone exists in the Earth’s stratosphere and is accountable for preserving humans from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Earth’s ozone layer is draining due to the presence of hydrochlorofluorocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere.
As the ozone layer shifts thin, it releases harmful rays back on Earth and can create skin and eye-related difficulties. UV rays also can adversely affect crops.
Solutions for Reducing Air Pollution
There are numerous solutions for air pollution reduction; some of them are listed below.
Utilize the Public Transportation
We should encourage people to utilize more and more public forms of transportation to diminish pollution. Also, we should try to make use of carpooling. If you and your partners come from the same region and have the exact timings, you can examine this option to conserve energy and money.
Better Household Practices
Reject fireplaces and wood stoves employed for heating houses. Use gas sticks in place of wood. Also, exclude the use of gas-powered gardening and lawn equipment. Evade setting fire to garbage, dry leaves, or other materials in your yard and lighting campfires in the open. Try to compost or mulch your yard rubbish. Use sanitation products and colors that are environmentally friendly.
Energy Conservation
Switch off lights and fans when you are running out. A considerable amount of fossil fuels is consumed to generate electricity. You can preserve the environment from degradation by diminishing the number of fossil fuels to be consumed.
Emphasis on Clean Energy Resources
One should switch to the use of clean energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, which are on the growth these days. Governments of different countries have been presenting awards to consumers who are engaged in installing solar panels for their houses. Unquestionably, this can go a long way to control air pollution.
Understand the Concept of Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle
Do not throw away things that are of no worth to you. Alternatively, reuse them for some other object. For instance, you can employ old containers to store grains.
Use Energy-Efficient Devices
CFL lights use less electricity than their equivalents. They live longer, spend less electricity, lead to lower electricity charges, and also assist you in decreasing pollution by utilizing less energy.
Various attempts are being made worldwide on governmental, industrial, and personal levels to control the intensity at which air pollution is increasing and recover a balance as far as the proportions of the ground gases are concerned.
This is a direct effort at slacking Global warming. We see a series of discoveries and experiments pointed at forming alternate and unconventional options to degrade pollutants. Air pollution is one of the giant mirrors of man’s follies and a difficulty we need to defeat to see a greater tomorrow.
How to Control Air Pollution and Protect Yourself?
Here, there are some pieces of advice, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, to reduce the risk of air pollution harm on your health.
Follow these Tips Every Day to Diminish Pollution
- Preserve energy at work, home, and everywhere.
- Consider an ENERGY STAR label when buying a home or office equipment.
- Carpool, utilize public transportation, bike, or walk whenever feasible.
- Follow gasoline refueling guidance for efficient vapor recovery, be careful not to spill fuel, and always tighten your gas cap securely.
- Consider buying portable gasoline containers labeled “spill-proof,” where possible.
- Keep car, boat, and other engines suitably tuned.
- Be sure your tires are correctly inflated.
- Use environmentally harmless paints and sanitation products whenever feasible.
- Compost or mulch or leaves and yard waste.
- Consider applying gas logs rather than wood.
On Days when High Ozone Levels are Supposed, Take these Extra Steps to Diminish Pollution
- Choose a more reliable commute, share a ride to work, or utilize public transportation.
- Combine tasks and decrease trips. Walk to duties when feasible.
- Avoid unnecessary idling of your vehicle.
- Refuel your vehicle at cooler times of the day.
- Preserve electricity and set air conditioners no lower than 25 centigrade.
- Defer gardening chores and lawns that use gasoline-powered equipment, or wait until evening.
On Days when High Particle Levels are Supposed, Take these Extra Steps to Diminish Pollution
- Decrease the number of travels you take in your vehicle.
- Decrease or eliminate wood stove or fireplace use.
- Avoid burning trash, leaves, and other materials.
- Avoid applying gas-powered garden and lawn equipment.

Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Types of Air pollution: All you should know
- Main Solution of Water Pollution in 2022
- 10 Main Causes of Water Pollution in 2022
- What is Water Pollution?
- 10 Types of Water Pollution in 2022 + PDF
- What is Negative Air Pressure: A Complete Guide



