Telecommunications such as radio, telephone, and television all use a method called multiplexing to transmit and receive information. Multiplexing was designed to send numerous analog signals or digital streams through one common transmission line. The process of combining the data streams is known as multiplexing and the hardware used for multiplexing is known as a multiplexer. In this article, Linquip will answer the question: “What is multiplexing and its types?”. Keep on reading for a complete answer.
What is Multiplexing?
Multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a popular networking technique that integrates several signals and transmits them over a single data link. The process of multiplexing divides a communication channel into several logical channels, allotting each one for a different message signal or a data stream to be transferred.
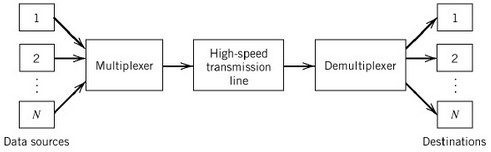
Multiplexing is achieved by using a device called Multiplexer (MUX) that combines “N” input lines to generate a single output line. As you see, the output is a compressed version of the input, multiplexing is an effective and inexpensive way to transmit and share information via telecommuting or a computer network. Often, the medium through which the multiplexed signal is transmitted can be shared, such as a telephone wire that transmits multiple phone calls. Once the stream reaches its destination, a process called demultiplexing returns the data stream to its original, decompressed state. The device that enacts demultiplexing is called a Demultiplexer (DEMUX).
The concept of Multiplexer and Demultiplexer is illustrated in the figure below.
Different Types of Multiplexing Techniques
- Analog
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
- Digital
- Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- Synchronous TDM
- Asynchronous TDM
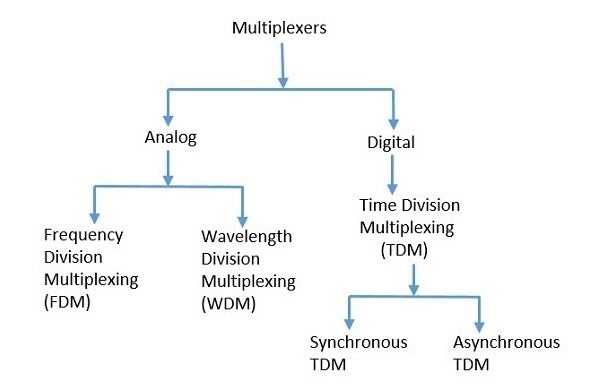
Multiplexing techniques can be classified into two types: Analog Multiplexing and Digital Multiplexing. They are further divided into FDM, WDM, and TDM.
Analog Multiplexing
The analog multiplexing techniques involve analog signals. The analog signals are multiplexed according to their frequency (FDM) or wavelength (WDM).
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
Frequency Division Multiplexing is a technique that uses various frequencies to combine many streams of data for sending signals over a medium for communication purposes. It carries frequency to each data stream and later combines various modulated frequencies for transmission. Television Transmitters are the best example of FDM, which uses FDM to broadcast many channels at a time.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is an analog technique in which many data streams of different wavelengths are transmitted in the light spectrum. If the wavelength increases, the frequency of the signal decreases. A prism, which can turn different wavelengths into a single line, can be used at the output of MUX and input of DEMUX. An example of WDM application is in optical fiber communications that use the WDM technique to merge different wavelengths into a single light for communication.
Digital Multiplexing
Digital multiplexing is applied to digital signals and has several types that are as follows.
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
The TDM is one kind of method for transmitting a signal over a channel of particular communication by separating the time edge into slots. Like single slot is used for each message signal. TDM is mainly useful for analog and digital signals, in which several channels with low speed are multiplexed into high-speed channels used for transmission. Depending on the time, every low-speed channel will be assigned to an exact position, wherever it works in the mode of synchronization. Both the ends of MUX and DEMUX are synchronized timely and at the same time switch toward the next channel.
The different types of TDM are described below.
Synchronous TDM
In Synchronous TDM, the input is connected to a frame. If there are ‘n’ number of connections, then the frame is divided into ‘n’ time slots. One slot is allocated for each input line. In this technique, the sampling rate is common to all signals and hence same clock input is given. The mux allocates the same slot to each device at all times.
Asynchronous TDM
In Asynchronous TDM, the sampling rate is different for each of the signals and the clock signal is also not common. If the allotted device, for a time slot, transmits nothing and sits idle, then that slot is allotted to another device, unlike synchronous.
Other Types of Multiplexers
- Code Division Multiplexing
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
- Space Division Multiplexing
- Polarization-division multiplexing
- Orbital angular momentum multiplexing
The other types of multiplexers are described below.
Code Division Multiplexing
Code division multiplexing (CDM) is a multiplexing technique that uses spread spectrum communication. In spread spectrum communications, a narrowband signal is spread over a larger band of frequency or across multiple channels via division. It does not constrict bandwidth’s digital signals or frequencies. It is less susceptible to interference, thus providing better data communication capability and a more secure private line.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of signal modulation that offers some important benefits for data links. So, OFDM is mainly used for several most recent wide bandwidth and wireless systems with high data rates like cellular telecommunications, Wi-Fi, etc.
OFDM uses a large number of carriers where each carrier holds low bit rate data which means it is very flexible to preferred fading, intrusion, and multipath effects and provides a high amount of spectral efficiency.
Space Division Multiplexing
In wired communication, space-division multiplexing, also known as space-division multiple access (SDMA) is the use of separate point-to-point electrical conductors for each transmitted channel. Examples include an analog stereo audio cable, with one pair of wires for the left channel and another for the right channel, a multi-pair telephone cable, a switched star network such as a telephone access network, a switched Ethernet network, and a mesh network.
Polarization-division multiplexing
Polarization-division multiplexing (PDM) is a physical layer method for multiplexing signals carried on electromagnetic waves, allowing two channels of information to be transmitted on the same carrier frequency by using waves of two orthogonal polarization states. It is used in microwave links such as satellite television downlinks to double the bandwidth by using two orthogonally polarized feed antennas in satellite dishes. It is also used in fiber optic communication by transmitting separate left and right circularly polarized light beams through the same optical fiber.
Orbital angular momentum multiplexing
Orbital angular momentum multiplexing is a relatively new and experimental technique for multiplexing multiple channels of signals carried using electromagnetic radiation over a single path. It can potentially be used in addition to other physical multiplexing methods to greatly expand the transmission capacity of such systems. As of 2012, it is still in its early research phase, with small-scale laboratory demonstrations of bandwidths of up to 2.5 Tbit/s over a single light path. This is a controversial subject in the academic community, with many claiming it is not a new method of multiplexing, but rather a special case of space-division multiplexing.
So, now you know the answer to the question “What is multiplexing and its types?”. If you enjoy this article in Linquip, let us know what you think by leaving a reply in the comment section. We will be more than glad to have your viewpoint on the article. Is there any question we can help you through? Feel free to sign up on our website where our experts are prepared to provide you with the most professional advice.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip: