In order to provide healthy air for breathing, ventilation is crucial. There are generally five types of ventilation. One of that, which is often mentioned as the most important one, is mechanical ventilation system. Although natural ventilation is the most common ventilation method, it is not considered the best strategy since homes are properly air sealed and energy-efficient nowadays. Furthermore, it does not have the ability of moisture control. Due to these deficiencies, mechanical ventilation has more fortune to win the competition.
Rather than depending on airflow through small holes or cracks in a home’s roof, walls, or windows, mechanical ventilation systems use ducts and fans to circulate fresh air. The use of HVAC Items necessitates the use of a mechanical ventilation system. Mechanical Ventilation Systems are available from a variety of Suppliers and Companies, as well as manufacturers and distributors, with several Mechanical Ventilation Systems For Sale on Linquip.
There is a comprehensive list of mechanical ventilation system services on the Linquip website that meets all of your needs. Linquip can connect you with a number of Mechanical Ventilation System Service Providers and experts who can help you. Linquip can provide you with a list of ventilation professionals and subject matter experts who can help you test your equipment.
Now let’s take a look at mechanical ventilation system.
What is a Mechanical Ventilation System?
If we employ fans’ power to provide fresh air in the building or room, it means we have a mechanical ventilation system. These systems utilize fans installed in air ducts or directly in windows or walls. The fans exhaust the polluted air to the ambient and supply clean air into the room. Different types of mechanical ventilation are available, which can be used for various purposes.
For choosing the system, one should consider the climate, level, and types of pollutants. For example, in hot and humid climates, it may be necessary to minimize or prevent intrusion rather than interstitial compaction (which, when hot and humid air penetrates a wall, ceiling, or floor from inside a building with a cold surface encounters) prevent. In these cases, a positive pressure mechanical ventilation system is often used. Conversely, in cold climates, exfiltration should be avoided, and negative pressure ventilation should be used to prevent intermediate condensation. A negative pressure system is often used for a room with locally produced pollutants, such as a bathroom, toilet, or kitchen.
In a positive pressure system, the room is under positive pressure, and the room air leaks out through a leak in the envelope or other openings. In a negative pressure system, the place is in negative pressure, and the room air is compensated by “sucking” the outside air.
In what follows, different types of mechanical ventilation systems and differences between them are elaborated.
Types of Mechanical Ventilation System
There are four types of mechanical ventilation, which can be employed in different situations. These types are exhaust-only ventilation systems, supply-only ventilation systems, balanced ventilation, and energy recovery systems. In what follows, each type is described comprehensively.
Exhaust-Only Ventilation System:
One of the subsets of mechanical ventilation is the exhaust only system. The principle of working of this system is based on depressurizing the building. It often does not have any particular component to pull outside air into the room. By decreasing the indoor air pressure below the outdoor air pressure, the outside air will enter the room through leakages in walls and windows.
The exhaust ventilation system is suitable for cold climates. If we employ this system in warm and humid summers, the reduced pressure may draw the moisture into the building and wall cavities, where it may cause moisture damages because of condensation.
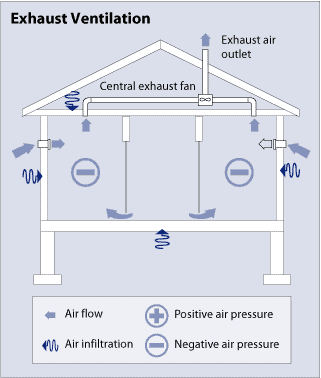
The proposed system is relatively easy to work with and does not require much Capex to install. Typically, it consists of a single fan that is connected to a centrally located home exhaust point. Therefore, the operating cost is low enough and makes the system more economical.
Another option for fan connection is to conjoin it to the ducts from various rooms– especially rooms with more pollutants, such as bathrooms and kitchens. Some passive adjustable vents can be installed on windows and walls to provide more fresh air and not rely on just leakages in building envelopes.
One concern of using exhaust ventilation systems is drawing pollutants, along with fresh air, into the house. For example, in addition to pulling in fresh outdoor air, they may draw in flue gases of a fireplace into the inner space.
Furthermore, exhaust ventilation systems can cause higher heating and cooling expenses compared with energy recovery ventilation systems since these types do not temper or eliminate moisture from the outside air before it enters the house.
Supply-Only Ventilation System:
The supply ventilation system employs a fan to pressurize the inside air and force outside air into the building. The polluted air in the rooms escapes through exhaust fan ducts and possible leaks in the building envelope.
This type of mechanical ventilation allows better control of the entering air in comparison with exhaust ventilation. By pressurizing the house, supply ventilation reduces the chance of pollutants entering the room and inhibits back drafting of combustion gases produced in fireplaces and other applications. They also allow the air entering the house to be dehumidified and filtered to remove dust.
The supply ventilation system shows better performance in hot and mixed climates since pressurizing the inside air may result in some moisture difficulties in cold winters.
In winter, the supply ventilation system allows hot indoor air to leak through unintentional openings in the ceiling or exterior wall. If the indoor air is humid enough, some moisture may condense in some parts of the exterior wall, causing decay and mold.
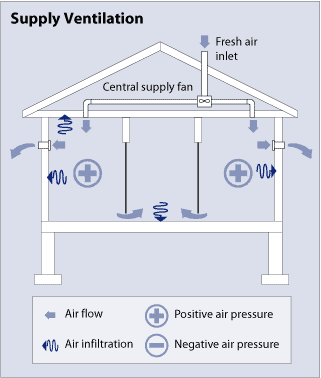
Like exhaust ventilation systems, supply ventilation systems do not temper or eliminate moisture before entering the home. Therefore, they may cause more heating and cooling costs in comparison with energy recovery ventilation systems. Because air enters the house in discrete places, it may be necessary to mix outdoor air with indoor air before delivery to prevent cold air from drawing in winter. Another option which should be kept in mind is the inline duct heater, but it may cause more operating costs.
Balanced Ventilation System:
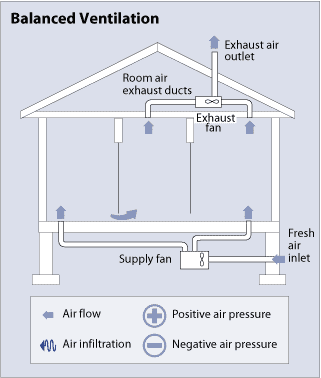
Another type of mechanical ventilation system is a balanced ventilation type. The properly designed balance ventilation system neither depressurizes the indoor air, like exhaust ventilation nor pressurizes it, such as supply ventilation. Even the ventilation system introduces fresh outside air and exhaust polluted inside air in approximately equal quantities. This system often utilizes two duct systems and two fans to do its job well. If supply and exhaust vents are placed in appropriate positions, the balanced ventilation system facilitates the proper distribution of clean air.
A typical balanced air conditioning system is designed to provide fresh air to the bedrooms and living rooms, where people spend most of the time. It removes air from places where most moisture and pollutants are generated, such as the kitchen, bathroom, and laundry room as well.
Like exhaust and supply ventilation systems, which are two common mechanical ventilation types, the balanced one also does not temper or remove moisture before entering the room. However, they employ filters and eliminate dust of outside air before entering the house.
Balanced ventilation systems can be installed in all climates. Nevertheless, they are more expensive because of applying two fans and duct systems.
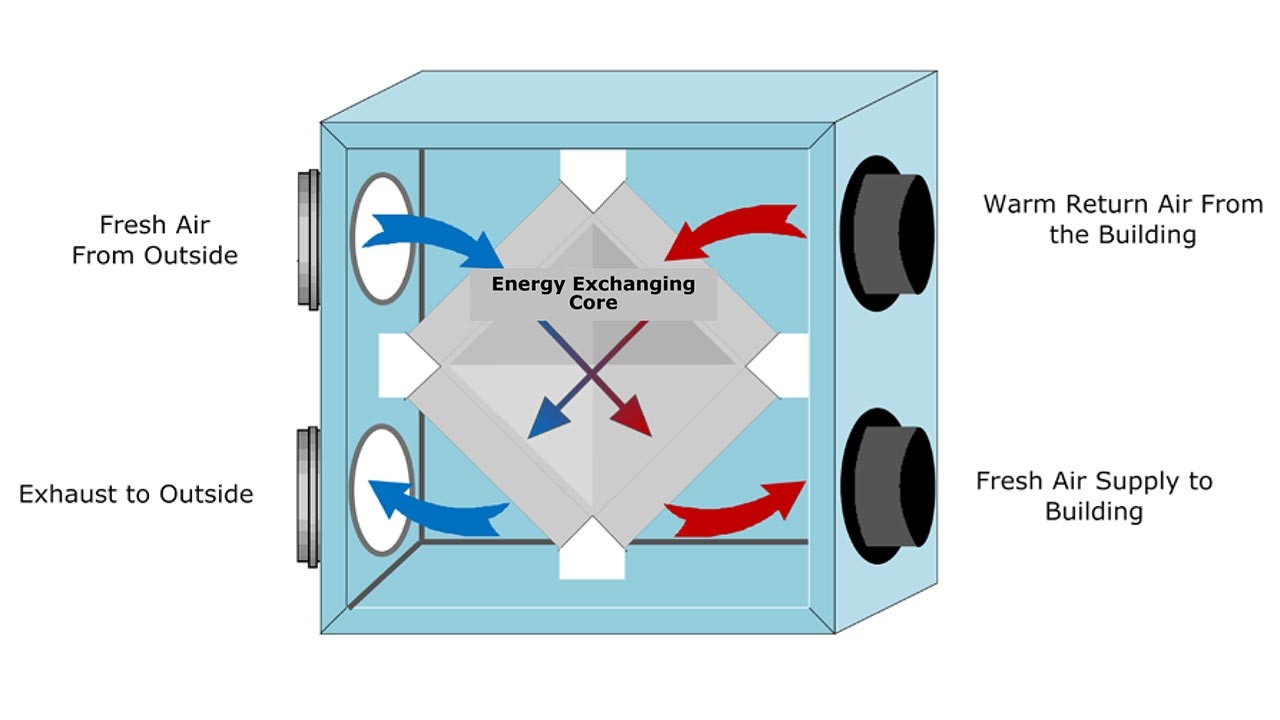
Energy Recovery Ventilation System:
Energy recovery ventilation is another subset of the mechanical ventilation system. It prepares a controlled way of ventilation to minimize waste energy and transfers heat from the warm exhaust air to the cold supply one. In this way, the cost of heating ventilated air decreases drastically.
This system is usually more expensive than other types of ventilation since it has more complexity in components and installation. Some energy recovery systems use share existing ductwork to manage the expenses. It also has more maintenance intensity and consumes more electric power.
Generally, you need a supply and return duct for each separate room. Ducts should be short and straight to reduce pressure drops. Furthermore, a duct with the correct size helps minimize pressure drop in the system and improve performance.
A critical point in using energy recovery systems in cold climates is that freezing and frost formation can damage the system, especially heat exchangers. So, they should be prevented from freezing and frost formation by means of embedded devices.
In addition, we should regularly clean energy recovery ventilation to prevent deterioration of ventilation rates and heat recovery and prevent mold and bacteria from forming on heat exchanger surfaces.
Advantages of Mechanical Ventilation
Each type of mechanical ventilation systems, like other systems, has specific advantages and disadvantages. Rather than the pros and cons of each kind of mechanical ventilation system, some more general benefits are listed below:
- It can easily be integrated with the air conditioning system.
- Indoor humidity and inside temperature are easily under control.
- Filtration system can be added to the mechanical ventilation system.
- Regardless of ambient temperature and wind, the desired flow rate can be accessed consistently.
- You just need electricity for it to work.
- The airflow direction can be controlled.
Disadvantages of Mechanical Ventilationss
Despite all the advantages mechanical ventilation system has, we cannot turn a blind eye to its drawbacks. Some of those weak points are mentioned below:
- If you ignore installing considerations, the inappropriate installation of a mechanical ventilation system may increase the maintenance costs dramatically.
- Backing up mechanical ventilation for a critical facility may be economically unreasonable.
- The utility service interruption or equipment failure often interrupts the regular operation of a mechanical ventilation system.
Because of these problems, mechanical ventilation systems may cause the spread of pollution in the area instead of being an essential tool for providing healthy air. So, be careful in employing them!
Download Mechanical Ventilation System PDF
Read More In Linquip
- 5 Types of Ventilation and All We Should Know About
- HRV vs ERV: Choosing Between Remarkable Types of Ventilation Systems
- Stack Ventilation: A Comprehensive Overview of The Principles and Applications
- Ventilation Design: Spectacular Tips You Need to Know Before
- Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV): Definition, Advantages & Installation
- Natural Ventilation: Types ,Advantages and Disadvantages
- Home Ventilation: Necessity, Types, and Strategies
- Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV): Installation, Types & Advantages



It was really helpful
Dear Fatimah
Thanks for your attention.
Wow I like this it has helped me alot
Thanks for visiting our website and leaving your comment! You are encouraged to visit Linquip Tech News, where you can find similar posts.
Thank you so much, very clear and helpful !
Thanks for visiting our website. We also encourage you to visit the Linquip website, where you can find numerous industrial equipment, along with companies and experts.