Types of Molding Machinery – The molding process is a method for shaping a material on the contours of a die or mold, frequently using a plastic molding machine. Other materials that may be formed this way include metal, rubber, and powder mixtures. One of the pieces of equipment that may be regarded as the foundation of such an investment in the field of plastics and industries related to plastic is a molding machinery. Just as there are several uses for each molding method, there are numerous distinct procedures for molding materials.
The Linquip is a source of information regarding molding machinery. No matter what situation you are in, we can assist you identify the appropriate molding machinery. Linquip provides a diverse range of Molding Machinery Products to ensure that you can find one that meets your demands.
On Linquip’s website, a comprehensive list of molding machinery is available to all OEM fleets. Linquip vendors can help you with this. Please contact Molding Machinery Experts to learn more about how to find a diverse choice of Service Providers who consistently supply high-quality products. If you want to find out how much a molding machinery will cost, the Linquip platform offers a free quotation request service from accessible Molding Machinery Suppliers and Companies.
Custom Plastic Molding
Thermosets and thermoplastics are the two main categories of plastics. These two kinds of plastic vary primarily in that thermosets permanently cure. This implies that the plastic cannot be melted back down to molten plastic once it has been shaped. Plastic will hold its shape after it has taken it. When plastic melts, it just burns. This contrasts with thermoplastics, which can be melted back down to liquid plastic after being cured into a shape and then reformed by additional curing.
Nurdles, which are small plastic pellets meant to facilitate transportation for commerce, are used to generate custom-molded thermoplastics. The nurdles are combined to make a molten bath, molded into the final form, and then dried when they are employed by a manufacturer to create a plastic application. The object is in its final shape after curing. Thermosets are delivered as raw liquid resin or powders since they cannot be melted down after curing.
On the other hand, metals, such as bar stock, pipe stock, and metal rods, are frequently supplied as stock. A formed raw metal product that comes in erratic sizes is called stock. It is delivered to producers so they may melt the metal down and utilize it for more rendering or final production, among other things. Other metal kinds, many of which are employed in specific molding processes, are transported in powder form and may be melted into a molten state. Metals and thermoplastics both have the ability to be melted down and reconfigured after setting.
A releasing agent is necessary for the majority of molding processes. A releasing agent is a kind of lubricant that lessens the chance that a material that has been molded would attach to the internal surface of the mold.

Types of Molding Machinery
10 Types of Molding Machinery include:
- Thermoforming Molding
- Vacuum Forming
- Injection Molding
- Compression Molding
- Transfer Molding
- Extrusion Molding
- Blow Molding
- Rotational Molding
- Hydroforming
- Laminating
There are a few characteristics that are shared by various molding techniques. One is the availability of a material that has to be shaped, usually in molten form. Another is the mold, which holds the design that will be imprinted onto the material. Last but not least, apply the necessary pressure to expand the material into the mold’s shape. Variables in these three constants play a role in how various molding techniques differ from one another. For instance, some techniques operate with various materials, some with various molds, and yet others employ various pressure sources.
Thermoforming Molding
Thermoforming involves the use of a vacuum to press thin sheets of thermoset or thermoplastic plastic into a mold. Thermoforming machines for plastic typically slide a sheet of plastic over a mold to hermetically bond the plastic to the pattern. The plastic is heated to a malleable temperature. The plastic is then drawn into the mold by use of a vacuum. Excess plastic around the mold edges is cut off using cutting equipment, and the plastic is then taken out of the mold. As a new sheet of plastic is placed in its position, the molded plastic is spread down the assembly line.
Vacuum Forming
For thermoplastics, vacuum forming, also known as vacuum forming, is a kind of thermoforming that differs in gauge capacity and application. Usually, only thin plastic sheets, or “film,” are vacuum-formed. The opposite of thermoforming, the film is stretched over a mold before being suctioned around it using a vacuum.
Injection Molding
Plastic pellets from High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) are used as the raw material for injection molding equipment. A nozzle is used to inject molten plastic pellets into the clamped mold of the injection molding machine after the resins have first been melted into a molten state.
The mold is instantly cooled to aid in the molten plastic’s setting once it has been poured into all of its cavities. The mold opens up to release the plastic material that has been precisely shaped to fit the mold chambers once the setting period has passed.
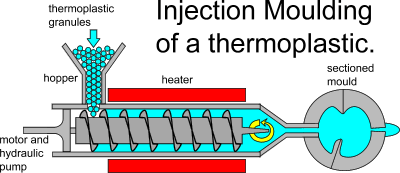
At each cycle of molten plastic injection, many injection mold compartments have the capacity to manufacture up to roughly 20–30 plastic caps or pieces.
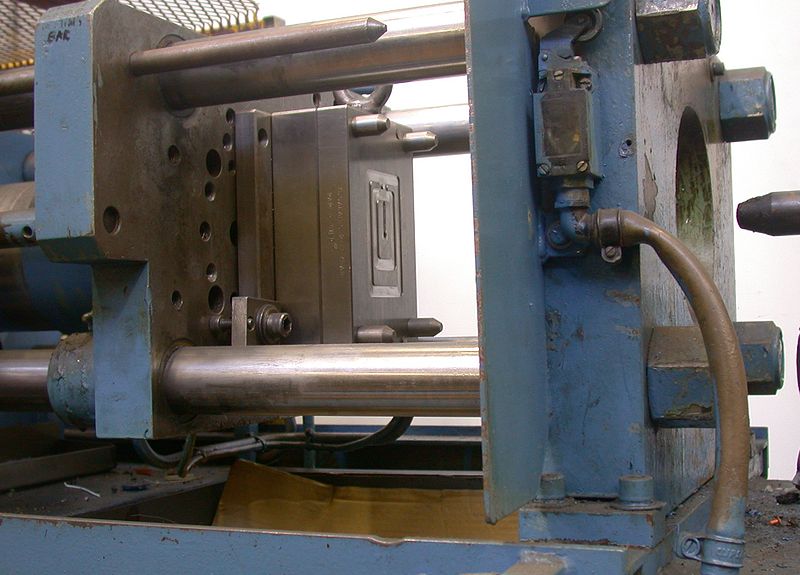

There are several injection molding technique variants, including:
- Cube molding
- Die casting
- Gas-assisted injection molding
- Liquid silicone rubber injection molding
- Metal injection molding
- Micro injection molding
- Reaction injection molding
- Thin-wall injection molding
Product made with an injection molding machine:
– Plastic bottle caps
– PET preform (a tube-like vial with a threaded neck)
– As well as other plastic items like plates, utensils, glasses, etc.
Compression Molding
In some respects, compression molding is the opposite of injection molding. The mold is filled with the molten plastic, which is then closed. Somewhere in the mold is an intake hole via which pressure is applied by another device. The final form is achieved when pressure drives the plastic outward into the mold’s hollow interior. Items created via compression molding frequently include a lot of “flashing,” or extra plastic, which needs to be removed. Rubber products can also be created via compression molding.
Three different mold types are available for compression molding:
- Flash molds,
- Positive molds, and
- Semi-positive molds.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding is similar to compression molding, except it uses a metal plunger to provide pressure. The molten substance is poured into the mold and sealed within. The material is forced to expand outwards and fill in the mold’s geometry by pushing it deeply into the mold using a metal plunger, which resembles a big shaft. On rubber or plastic, transfer molding is an option.
There are two types of transfer molding process:
- Pot transfer molding, and
- Plunger transfer molding.
Extrusion Molding
One of the few molding techniques that may be used on hot or cold materials is extrusion. A die is utilized during extrusion procedures as opposed to a three-dimensional mold. A die is a two-dimensional hole with a specific shape through which material is pressed, or extruded. The substance that is extruded—typically a metal like aluminum or a plastic—takes on the geometry of the die. While multiple pieces of the same size are produced by semi-continuous extrusion, very lengthy sections are produced by continuous extrusion.
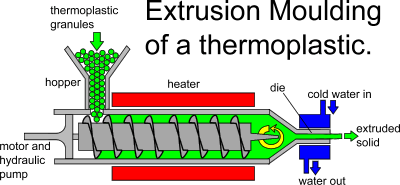
There are several types of extrusion methods, including:
- Cold extrusion,
- Hot extrusion,
- Friction extrusion, and
- Micro extrusion.
Items produced by an extrusion molding machine:
– Plastic rods.
– Plastic pipes
Blow Molding
While the extrusion molding machines utilize PET preform (which is created by the injection molding machines) as their raw material for the manufacturing of plastic bottles, the injection mold machines use resin as their raw material for the creation of plastic components.
The PET preform is heated in a heating chamber during the initial stage of operation of the extrusion molding machine, which helps to soften the PET preform. When the PET preform reaches the correct temperature, it is instantly withdrawn from the heating chamber and placed into the mold, where its threaded neck is hand-held. A stretcher is inserted into the bottle to extend it to the entire length of the mold once the bottle has been correctly fitted and the mold has closed. A plastic bottle that may be used for packing cream, liquid soap, or water is created by forcing compressed air into a stretched PET preform. This causes the PET preform to fill up and take on the precise shape of the mold.
There are three types of blow molding processes:
- Injection blow molding,
- Extrusion blow molding, and
- Injection stretch blow molding.
The end product of a blow molding machine:
– Plastic vial or bottle,
– As well as other hollowed plastic materials.

Rotational Molding
The plastics molding technique known as rotational molding, or rotomolding, is excellent for generating hollow objects. Although it is a casting technique, it does not utilize pressure as most other plastics processing does. To manage the necessary pressure to fill the mold, rotational motion is really employed in rotational molding. Plastic is melted and sealed inside a mold. Then, as the mold turns, the molten plastic drips down the sides and fills in all the cracks and patterns of the cast.
A wide variety of goods are produced using the rotomolding process. Because almost any shape may be created, the approach provides the product designer with a tremendous lot of creative freedom. Moldings have literally hundreds of applications, and there are practically no size constraints. Because the process’s molds don’t need to resist pressure, they are reasonably cheap and may be produced in relatively short runs at a very low cost.
There are several commercial rotational molding machines available:
- Rock and Roll Machines
- Clamshell Machines
Hydroforming
A metal-specific molding process called hydroforming employs water pressure to push metal into a dye or mold. The metal is enclosed inside the mold or dye machine after being heated to a malleable but not molten state. High hydraulic pressure water may be pushed in via a small opening. The metal is forced to fill the geometry of the cast by the intense pressure of the water in the mold. The workpiece is then ejected once the water has been drained. Explosive hydroforming is a kind of hydroforming that uses explosives. In this technique, the detonation of a small explosive exerts pressure on the water.
There are two types of hydroforming:
- Sُheet hydroformingو and
- Tube hydroforming.
Laminating
Laminating is a simple kind of plastic molding that involves applying pressure to a laminated plastic sheet to a substrate. On occasion, the laminate will overhang the substrate, forcing a second laminate sheet from the opposite side to attach to the first sheet. Either heat or physical pressure from a block is used to bind the plastic to the substrate.
Additional Information on the Molding Process
Molding procedures vary because different products necessitate different techniques and molding equipment. For example, blow molding and rotational molding are effective at producing hollow plastic goods such as bottles and cups, whereas laminating gives an appealing sheen to a product’s surface. The capabilities of the molding technique in relation to the intended final product should be taken into account while choosing a molding process. The time required for manufacturing varies depending on the molding technique. Rotational molding often works with polymers that take a long time to cure, and the process itself takes significantly longer than compression molding.
FAQs about Types of Molding Machinery
-
How Is Extrusion Output Determined?
The drag flow may be used to estimate an extruder’s output in lb/hr: 2.64 x D²Nhρ. The diameter (D) and channel depth (h) are in inches, the screw speed (N) is in rpm, and the melt density (ρ) is in gm/cc.
-
What Exactly Is Injection Pressure?
The pressure at which the mold fills is known as the injection pressure, sometimes referred to as the first-stage pressure. The pressure that is kept on the melt after it has been put into the mold, up until the gate freezes or the pressure is released by a cycle timer-controlled mechanism.
-
What Are The Crucial Factors In The Blow Molding Process?
Melt Temperature: Modifies the material’s viscosity. Extruder Speed: This parameter controls how quickly the parison is produced. Blow Time – Although the product is formed by blowing, maintaining pressure on it maintains it in touch with the mold and speeds up cooling.
-
What Is The Recommended Minimum Temperature For Compression Molding?
With a curing period of three minutes, a typical compression molding procedure is carried out at mold temperatures of 350°F and 100 psi (180°C and 700 kPa). The mold is opened and the plastic package is pulled out when the material has dried.
Download Types of Molding Machinery PDF
There is an option to download the article in PDF format if you find that to be more convenient for you. You can download the file by clicking on the following link.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- The 10 Best Mini/Benchtop Milling Machine
- 10 Best CNC Machines & Routers for WoodWorking
- 10 Types of CNC Machine + Applications & PDF
- 13 Parts of CNC Machine + Function & PDF: A Clear Guide
- What Is CNC Machining & How Does It Work? (A Comprehensive Guide)
- 11 Types of Drilling Machines and Their Usages



