As one of the basic passive components, inductors fill an important role in electronics applications, from starting engines to delivering power to your house. If you don’t know much about inductors, we will provide you with complete information as well as answering the question ‘what is inductor?’. Read this new blog in Linquip to find out more.
What is Inductor?
An Inductor is a passive type electrical component consisting of a coil of wire designed to take advantage of the relationship between magnetism and electricity by inducing a magnetic field in itself or within its core as a result of the current flowing through the wire coil. In other words, an Inductor is an electrical device that possesses the inductance.
Inductor Working Principle
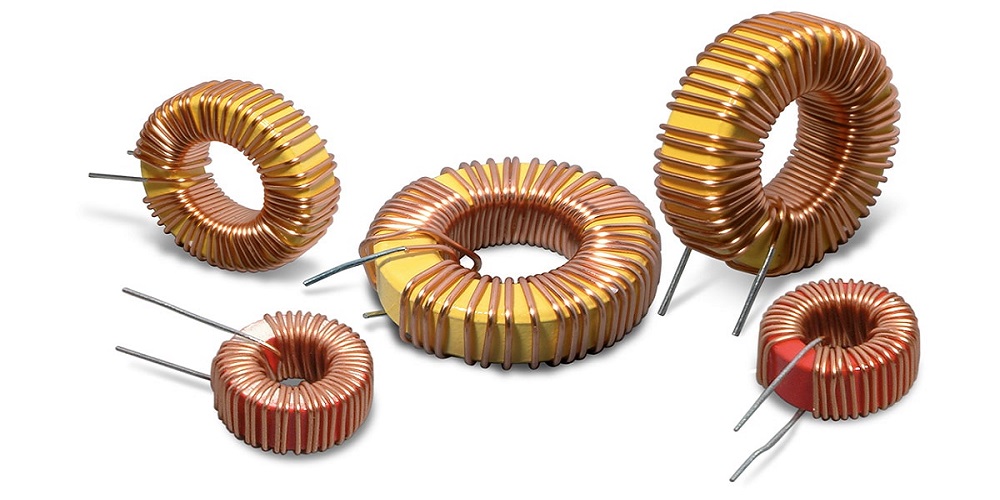
The inductor is an electrical device used for storing electrical energy in the form of a magnetic field. It is constructed by wounding the wire on the core. The cores are made of ceramic material, iron, or air. The core may be toroidal or E- shaped.
The coil-carrying the electric current induces the magnetic field around the conductor. The intensity of the magnetic field increases if the core is placed between the coil. The core provides the low reluctance path to the magnetic flux.
The magnetic field induces the EMF in the coil which causes the current. And according to Lenz’s law, the causes always oppose the effect. Here, the current is the cause, and it is induced because of the voltage. Thus, the EMF opposes the change of current that changes the magnetic field. The current which reduces because of the inductance is known as the inductive reactance. The inductive reactance increases with the increase of the number of turn of coils.
Inductor construction
An inductor usually consists of a coil of conducting material, typically insulated copper wire, wrapped around a core either of plastic (to create an air-core inductor) or of ferromagnetic material; the latter is called an “iron core” inductor. The high permeability of the ferromagnetic core increases the magnetic field and confines it closely to the inductor, thereby increasing the inductance.
The inductance of an Inductor is highly dependable on multiple factors, such as the number of turns of wire, the spacing between the turns, number of layers of turns, type of core materials, its magnetic permeability, size, shape, etc.
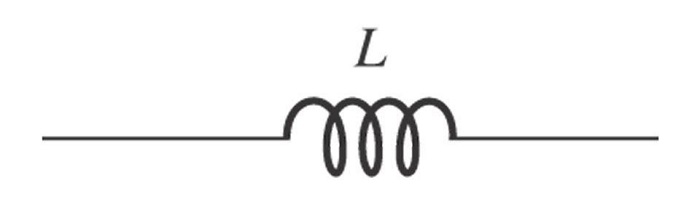
Inductor Symbol
The inductor is characterized by the value of inductance which is the ratio of voltage (EMF) and current change inside the coil. The alphabet ‘L’ is used for representing the inductance and it is measured in Henry which is named after Joseph Henry, an American scientist. The figure below shows the symbolic representation of the inductor.
The electric current flowing through the coil generates the magnetic field around it. The magnetic flux linkage Φ generated by a given current I depends on the geometric shape of the circuit. Their ratio defines the inductance L:
If the current flow through an inductor is changed at the rate of one ampere per second and 1V of EMF is produced inside the coil, then the value of inductance will be 1 Henry.
The inductance of the circuit depends on the current paths and the magnetic permeability of the nearer material. The magnetic permeability shows the ability of the material to forms the magnetic field.
Note that in Electronics the inductor with a value of Henry is rarely used as it is a very high value in terms of the application. Typically, much lower values like, Milli Henry, Micro Henry, or Nano Henry are used in most of the applications.
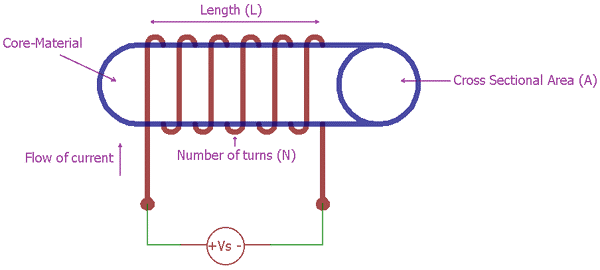
Inductor Diagram
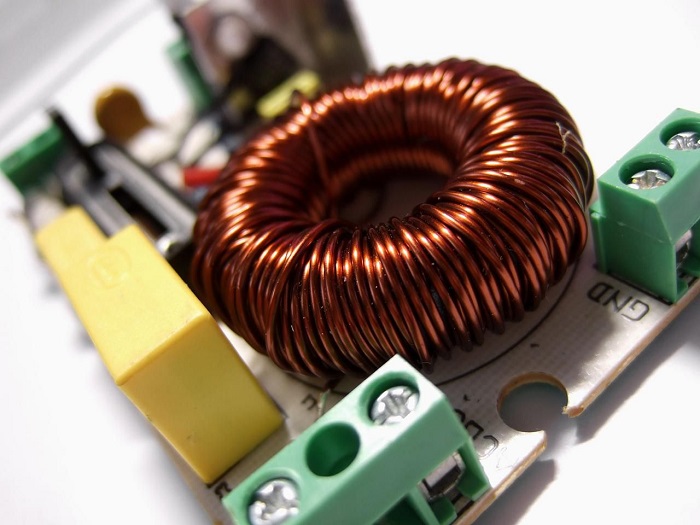
One generic, standard inductor construction and working diagram can be demonstrated as a copper wire wrapped tightly across a core material. In the below image, copper wire is closely wrapped across a core material, making it a two-terminal passive inductor.
Why Does an Inductor block AC rather than DC?
To answer this, one needs to understand the Lenz law. As per the Lenz law, the direction of current induced in a conductor due to the change in the magnetic field is such that it creates a magnetic field that opposes the change that produced it.
So, there are two types of applications. The first is to apply DC across the inductor and the other one is to apply AC across the inductor.
When the alternating current is applied across the inductor, the AC changes the current flow which is opposed by the inductor by increasing the reactance. The higher the frequency of AC, the higher the rate of change current and the higher the blocking effect from the inductor.
But, at the time DC is applied through the inductor, the inductor act as a near short circuit with very low resistance. In a steady-state DC flow, the rate of current changes is zero which further makes the di/dt zero. So, there was no voltage is induced and the Inductor does not oppose the flow of DC.
Inductor Application
Inductors are used in a wide area of applications that are as follows:
Tuning Circuits
With the help of inductors, the tuning circuits can select the desired frequency. The capacitors type along with the inductor are used in various electronic devices such as radio tuning circuits, a television to modify the frequency and help to select within multiple channels of frequency.
Inductive Sensors
The inductive proximity sensors are very reliable in operation and is a contactless sensor. Inductance is the main principle behind it in which the magnetic field in the coil will oppose the flow of electric current. The proximity sensors mechanism is used in traffic lights to detect traffic density.
Energy Storage Devices
Inductors can store energy for a small period because the energy which is being stored as a magnetic field will be gone when the power supply is removed. Uses of inductors can be seen in computer circuits where power supplies can be switched.
Induction Motors
In induction motors, the shaft in the motor will rotate due to the presence of the magnetic field produced due to alternating current. The speed of the motor can be fixed according to the frequency of the supply of power from the source. The use of inductors in the motor’s speed can be controlled.
Transformers
A combination of multiple inductors with a shared magnetic field can be designed into a transformer. One of the major uses of transformers can be seen in power transmission systems. These are used in decreasing or increasing the power transmission as step-down or step-up transformers.
Inductive Filters
Inductors when combined with capacitors will be used as filters. The input signal’s frequency while entering the circuit is limited by the use of these filters. With the increase in the frequency of supply, the inductor’s impedance increases.
Chokes
As we are aware that when AC flows through inductors, it will create a current flow in the opposite direction. This results in the inductor choking the AC flow and passing the DC. This mechanism is used in the power source where the AC supply is converted into DC.
Ferrite Beads
We have seen ferrite beads used in computer parts and in charging cables of mobile. Inductors used in ferrite beads help in reducing the frequency of the radio interface which the cable creates.
Relays
Relay behaves as an electrical switch. With the use of an inductor coil in the switch, there is a magnetic field produced wherever the switch comes in contact with the flow of AC.
So, now you know the answer to the question “what is inductor?”. If you enjoy this article in Linquip, let us know what you think by leaving a reply in the comment section. We will be more than glad to have your viewpoint on the article. Is there any question we can help you through? Feel free to sign up on our website where our experts are prepared to provide you with the most professional advice.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- A Useful Guide to Different Types of Inductors
- Difference between Capacitor and Inductor- Capacitor vs. Inductor

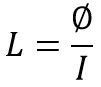




33uh Faridcore d class amplifier used