A pressure transducer, frequently named a pressure transmitter, is a transducer that transforms pressure into an analog electrical signal. Despite numerous types of pressure transducers, one of the most prevalent is the strain-gage base transducer.
Find all the info you need on pressure transducers on Linquip’s website. Linquip’s pressure transducers experts are standing by to assist you with any questions you may have. Start by reading Linquip’s article entitled, “What Is Transducer?“.
Register as a Linquip Expert if you wish to use all of the features offered by Linquip. How does Guest Posting on Linquip sound to you? Here is how you can submit your content as a guest on Linquip.
Pressure conversion into an electrical signal is accomplished by the physical deformation of strain gauges, which are bonded into the pressure transducer’s diaphragm and wired into a Wheatstone bridge arrangement. The pressure employed to the pressure transducer delivers a diaphragm deflection, which proposes strain to the gages. The strain will generate an electrical resistance change proportional to the pressure.
Working Principle of Pressure Transducer
The most popular pressure transducer structures comprise a force collector such as an elastic diaphragm and a transduction component that employs a dependent resistive, inductive, or capacitive method to produce an electrical signal. The type of electrical device utilized ascertains the components used to produce the pressure sensor.
Pressure transducers utilize strain gauges to measure the force operating on them. The strain gauges withstand deformation, and this deformation produces a variation in voltage generated by it. The pressure measurement is based on the degree of variation detected in the voltage.
There are also exceptional pressure transducers that apply capacitance or piezoelectric sensors rather than the strain gauges. They are preferred based on the range, work environment, and accuracy expected from the pressure sensor. To learn more about how a pressure transducer works, click here.
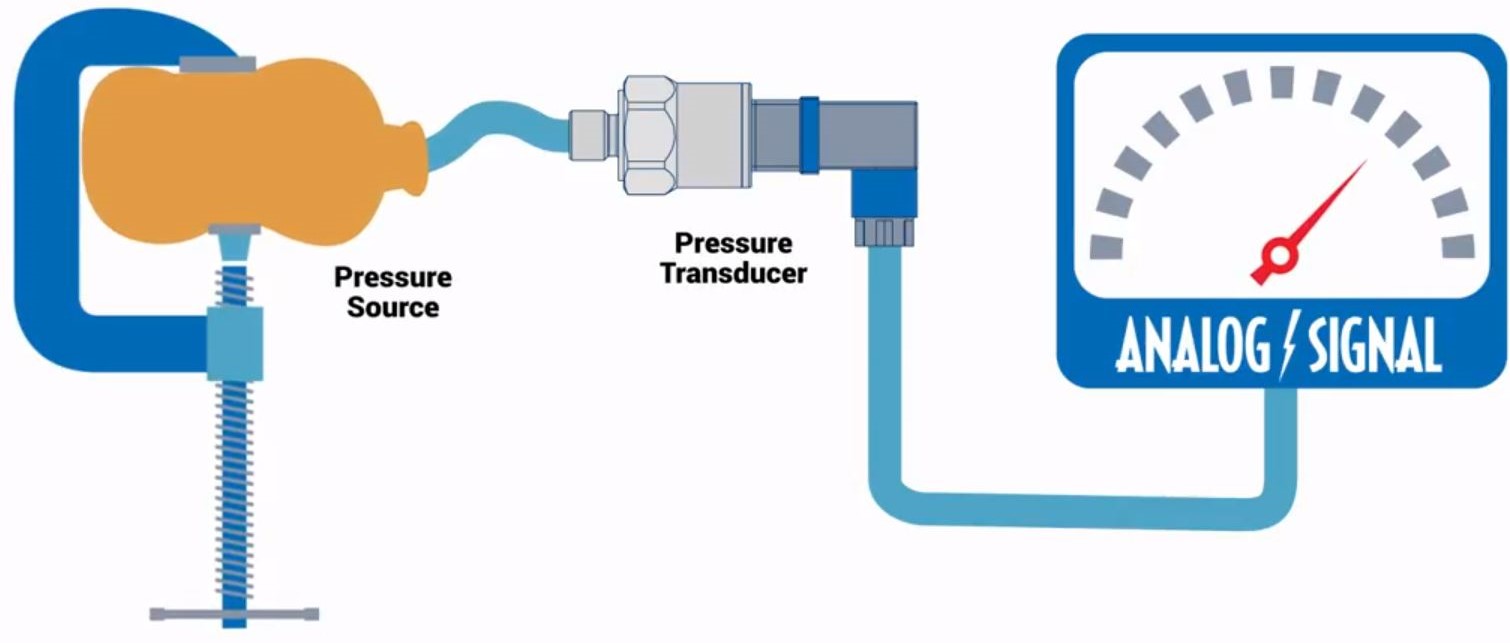
How does a static pressure transmitter work?
Static pressure transducers estimate the pressure of a stagnant fluid, which are the most prevalent pressure monitoring tools.
When a fluid exerts pressure on a pressure transducer, the strain gauge (or sensor) becomes deformed. This deformation proceeds in the variations of voltage. The greatness of variation agrees with the strength of the pressure. Once the pressure discharges, the strain gauge goes back to its initial configuration.
Piezoelectric pressure transducers are an illustration of dynamic pressure or non-static transducers. They cannot measure static pressure; alternatively, they measure pressure variations in real-time.
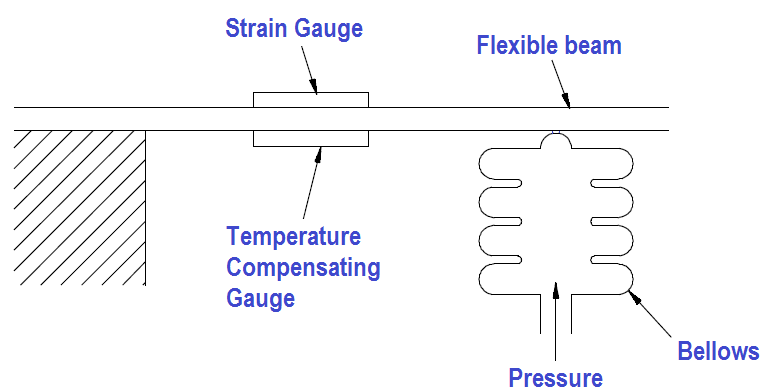
Piezoresistive strain gauge Pressure Transducer
A conventional piezoresistive strain gauge pressure transducer uses strain gauges bonded to a flexible diaphragm so that any variation in pressure produces a small deformation, or strain, in the diaphragm substance. The deformation alters the strain gauges’ resistance, typically regulated as a Wheatstone bridge, presenting a convenient conversion of the pressure measurement into a practical electrical signal.
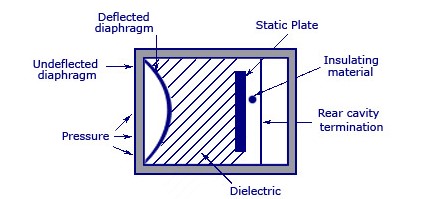
Capacitance Pressure Transducer
A variable capacitance pressure transducer possesses a diaphragm and another electrode attached to an unpressurized surface with a gap of a specific distance within the diaphragm and the electrode. A variation in pressure extends or narrows the gap, which alters the capacitance. This change in capacitance is then transformed into a proper signal.
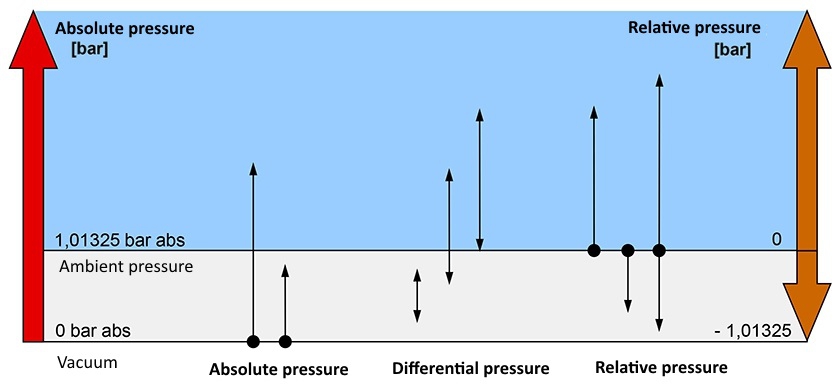
Types of Pressure
Three pressure references are defined for measuring pressure. Although there are other types, like sealed or vacuum gage, all can be categorized into these three classes: Absolute pressure, Gauge pressure, and Differential pressure.
Absolute Pressure
An absolute pressure measures the pressure relative to a complete vacuum, applying absolute zero as a reference point. A barometric pressure transducer is a prominent example. These also involve a sealed gauge, where the signal has been offset to meet the gauge pressure at construction time.
Gauge Pressure
A gauge pressure measures the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. A tire pressure sensor is an example of a gauge pressure measurement equipment. It also includes vacuum sensors, whose signals are inverted so that their signal is positive when the determined pressure is under atmospheric pressure.
Differential Pressure
A differential pressure transducer measures the difference between two pressures on each side of the sensor. A liquid pressure transducer is an obvious example where the fluid levels over and under the liquid are measured.
Types of Pressure Signal Outputs
A pressure transducer generates an electrical output signal comparable to the pressure attached to an electrical source and a pressure source. This may be in the form of current, voltage, or frequency. There are four distinct output parameters available, which a summary of them and their best usage conditions are mentioned below.
Digital Pressure Transducer
A digital signal presents more versatility than analog signals; usually, they are termed smart devices since they offer greater functionality than other sensor types.
Smart sensors can regularly express their location, log data, calibration information, detect anomalous events, or activate alarms. When determining a digital output, because there are many communication protocols accessible, it’s essential to select a compatible protocol with your employing system. Depending on the protocol, the transmission ranges can be even more than a mile. These types of sensors are decent in smart sensing and long transmission distance applications.
Millivolt Output Pressure sensor (ratiometric)
In this type of output signal, the actual output is proportional to the pressure transducer input excitation or power directly. If the excitation alternates, the result will also vary. Because of its dependency on the excitation level, controlled power supplies are recommended for millivolt transducers.
The sensor should not be in electrically noisy conditions since the output signal is so weak. However, these devices can readily handle harsher environments than other output types because of the output’s lack of signal conditioning and compact design. They can be employed in short distance applications when there is minimum electrical noise or a more enduring pressure sensor is needed to confront a harsh environment.
Voltage Pressure transmitter
In this sort of pressure sensor, the output is ordinarily 0-5dc or 0-10Vdc and presents a higher output compared to a millivolt transducer because of its integral signal condition.
Despite model-specific, the transducer’s output is not usually a direct function of the input signal. This implies uncontrolled power supplies are often sufficient as long as they fall within a particularized power range. They have a higher-level output and are consequently not as sensitive to electrical noise as millivolt transducers. They can be utilized in industrial environments with a relatively high level of noise.
mA Output Pressure transmitter
The mA is the most popular output in use. The signal can differ from 0 to 4 mA to 20 mA and is created as a two-wire establishment where the power supply lines produce voltage to the transducer, and the transducer regulates the current in the circuit make the signal.
This configuration presents the signal more immune to electrical impedance and enables long cable runs surpassing 1000 feet. They are used in environments with high electrical intervention or where long transmission ranges are required.
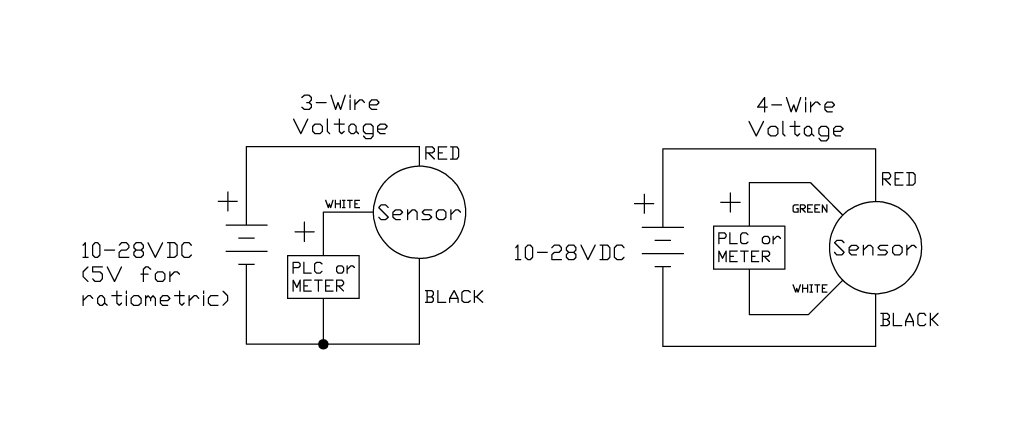
To learn more about pressure transducer types, visit here!
Choosing an Appropriate Pressure Transducer
You are still to select what type of pressure transducer or pressure transmitter you require?
As mentioned before, there are various types of pressure transducers for a diversity of applications. Each pressure transducer has several aspects that will influence how it operates and the applications the pressure transducer operates best for. When choosing a pressure transducer, these six criteria should be taken into account:
Application and measurement type
The standard type of pressure measurement involves: Absolute, gauge, vacuum, differential, bidirectional, and sealed gage. The application restricts the most suitable measurement type.
Pressure range
Seemingly the most critical decision in choosing a pressure transducer is the range of the input signal. For selecting an appropriate pressure transducer based on the measuring pressure range, one must keep in mind two contradictory considerations:
- The accuracy of the instrument and its protection from overpressure must be considered. From a precision point of view, the range of a transmitter should be sufficiently low, i.e., standard operating pressure near the middle range. So that error, ordinarily a percentage of full scale, is minimized.
- On the other hand, one must always admit the consequences of overpressure damage due to defective design, operating errors, or failure to isolate the instrument during pressure-testing and start-up. Therefore, it is essential to designate the required range and the amount of overpressure protection required.
Process media
The process fluid is another crucial factor in selecting an appropriate transducer. Often regarded as the “wetted parts,” these materials should be chosen to agree with the fluid being measured. For environments with clean, dry air, just about any material is permitted. However, for conditions utilizing sea-water, high nickel content alloys such as INCONEL® alloy 718 (UNS N07718) should be respected. Other popular materials comprise 316 Stainless steel and 17-4 Stainless steel. Also, if a sanitary fitting is needed, it should be taken into account.
Temperature range and installation environment
Very high temperature or vibration variations restrict what transmitters will function correctly. For temperature extremes, thin-film technology is preferred. The extreme temperatures also produce errors in the output of the transducer.
High vibration environments support smaller un-amplified traducers. The transducer housing should be chosen to match both the electrical area classification and the particular installation’s corrosion conditions.
Corrosion protection must be considered, both splashing of corrosive liquids or exposure to corrosive gases outside the housing.
This is typically accomplished either by placing them inside purged or explosion-proof houses or intrinsically safe designs. If a compact size is needed, an unamplified transducer is the best choice.
Accuracy
Pressure gauges come in many various accuracies. The accuracy of typical pressure transducers could differ from 0.5% to 0.05 % of the full-scale output. Higher accuracies are wanted when it is essential to read shallow pressures for critical demands.
Output
There are diverse types of outputs for pressure transducers, which was discussed earlier. In general, it is crucial to consider the restrictions and advantages of each output to ascertain the best output type for a specific application.
Pressure Transducer Applications
In what follows, some principle applications of pressure transducers are mentioned:
- These transducers are suitable in any liquid power application, which needs an accurate and high-resolution force determination.
- These transducers are employed where a force measurement is needed with a joined digital display.
- These transducers are utilized in closed-loop pumps for checking pump operation characteristics.
- These transducers are applied as an electronically changeable pressure switch.
- These transducers are appropriate within closed-loop applications like electronic pressure compensation, which calculate force upstream and downstream of a comparable metering tap to measure pressure fall accurately.
Pressure transducers are intended to use in industries. However, several problems happen due to inappropriate fitting. While troubleshooting this issue, the device must be provided in the correct place. If the transducer prevents working while working, determine the transmitted ampere unless raw voltage at no pressure from the transducer and also contain full capacity at the pressure. If the signal is not modified, we can understand that the device is not reacting to pressure. In some states, the transducer’s problems can be managed by repairing, recalibration; otherwise, this transducer may be replaced.
Pressure Transducer Advantages and Disadvantages
Here are some pros and cons of employing pressure transducers:
Advantages:
1) They are economical, robust, and fast response.
2) They have excellent accuracy, great stability, regulated output, and appropriate linearity.
3) They are fast response, highly sensitive, and tiny size measurement instruments.
Disadvantage:
1) They have moderate accuracy subject to drift or instability.
2) They have delayed response to shock and vibration conditions.
3) They work at a narrow temperature range, with moderate accuracy and sluggish response.
4) They are relatively sensitive to environmental conditions.
Download Pressure Transducer PDF
To make it easier for you to access this article, we have uploaded a PDF file for you to download and save on your hard drive.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Photoelectric Transducer: Application & Working Principles
- What is a Differential Pressure Sensor?: An Ultimate Guide
- An Easy Overview of Types of Pressure Gauges
- What Is Pressure Measurement?
- A Complete Answer To What Is A Pressure Gauge
- What Is a Pressure Transducer? A Simple Descriptive of the Definition, Working Principle, and Considerations
- Important Detailed Information About The Types of Transducers
- Active Transducer: All You Should Know About
- Transducer vs. Sensor: Basic Differences & Advantages of Them
- Temperature Transducer: Definition, Working Principle, and Types
- What are the Main Benefits of an Ultrasonic Transducer?
- All You Need to Know about Transducer
- Types of Sensors Detectors/Transducers: An Entire Guide
- Resistive Transducer: Working Principle & Example




Very nice and informative article
Do you understand the unbelievable energy of solar solar batteries? I did some research study online and figured out that this innovation can really help create electricity! Would like to hear your thoughts on it.
Thanks for sharing your experience with us, Ethan! You can also visit our industrial directories, where you can find thousands of various industrial equipment based on your application and demand.