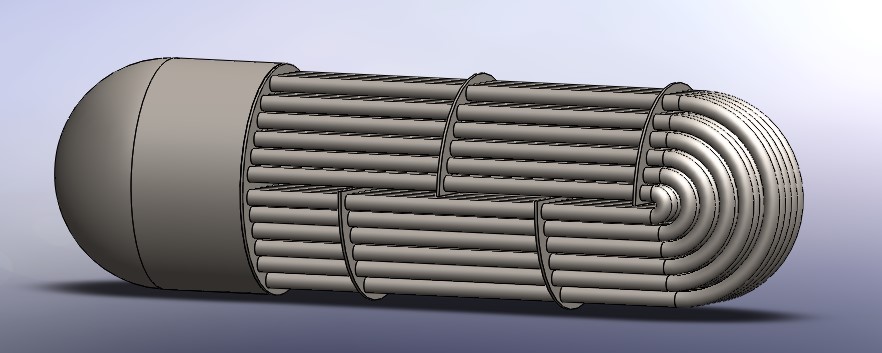
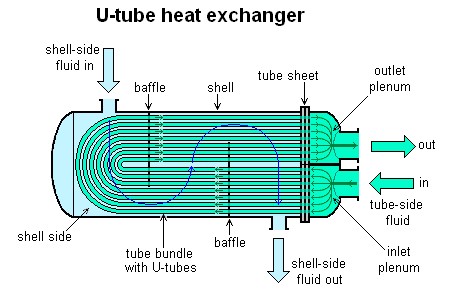
Many heat exchangers are U-shaped to maximize tube surface and heat exchange in a confined room. A u-tube heat exchanger or let’s say a u-tube configuration also makes it simple to enter the package. This article will provide readers with an introduction to one of the most common heat exchangers, the u-tube heat exchanger. Don’t miss it in Linquip.
What is u-tube heat exchanger?
U-tube heat exchanger is a form of tube and shell heat exchanger that is used in petroleum and chemical machinery. The tube box, casing, and tube buddle are the key components of a u-tube heat exchanger. Furthermore, drying is simple following the hydro test of the u-tube heat exchanger.
Both of the front header types may be used in a u-tube heat exchanger, and the rear header is usually an M-Type. The U-tubes allow for limitless thermal expansion, the tube bundle may be removed for cleaning, and small bundle-to-shell clearances are possible. However, since mechanical cleaning of the tubes is difficult, this type is normally used only when the tube side fluids are clean. The u-tube design has the drawback of not being able to provide pure counter-flow unless an F-Type Shell is used. Besides, u-tube designs are limited to an odd number of tube passes. This can be one of the disadvantages of u-tube heat exchanger.
On the other hand, about u tube heat exchanger advantages we need to say that the benefits stem from its compact size, which is also very powerful. Because of the U-shape, heat stress can be accounted for. A heat exchanger with U-tube packages takes up slightly less volume than a straight tube heat exchanger of the same design due to the bent individual tubes. Here also the concept of u tube vs straight tube heat exchanger comes to the scene. During the action, u-tube heat exchanger often provides only a low-pressure loss. Stainless steel can help to reduce corrosion and deposits. As a result, the number of repair cycles is greatly decreased. Additionally, a worn tube package may be replaced. If the input temperatures of the two media are very different, the material and construction must withstand extremely high heat stresses. As a result of the temperature differential, the metal expands at different points and to different extents, and cracks will form if the design is flawed. Because of the U-shape of the tube bundle, the heat exchanger can adjust for certain heat pressures very well and is hence well suited for operation with two output media at very different temperatures. Baffles are used in tube package heat exchangers to improve heat exchange.
Yes! There are more about u tube vs straight tube heat exchanger. Any manufacturer would have to decide whether to use a straight tube or a u-tube exchanger. The construction of the tube is important. If a manufacturer selects a tube design that is not appropriate for the application, it can result in exchanger damage or difficult-to-clean fouling. Both u-tube heat exchanger and straight heat exchanger are widely used in a variety of sectors, including food and beverage, chemical, and pharmaceuticals, and each has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Except for the tube configuration and the rear bonnet, they are similar.
Let’s discover the advantages of straight tube heat exchanger first.
Advantages of straight tube heat exchanger
One of the most significant advantages of the straight tube heat exchanger is its simplicity. Straight tube exchanger is also common because of its flexibility. Straight tube exchanger allows for pure countercurrent flow within the exchanger without the need for a second one to be connected in series to the first. An F-type two-pass shell with a longitudinal baffle is favored over an E-type in these situations. The baffle divides the two currents. As the cold and heat streams travel in opposite directions, this is referred to as countercurrent movement. For all stages in the exchanger, the hot stream should be colder than the cold stream, though the cold stream’s exit temperature might be greater than the hot stream. Co current flow, on the other hand, defines the passage of hot and cold streams in the same direction. The cold stream must always be lower than the hot stream in this setting. This means that the cold stream’s outlet temperature must be slightly lower than the other. This is impossible to do when the streams are going in the same direction, so many manufacturers resist co current designs.
u tube heat exchanger advantages
Although straight tube heat exchanger has many advantages, it can fall short in certain ways. This is one of the reasons why the u-tube heat exchanger is so popular. While a straight tube design is safer since the tubing does not need to be curved, as with U-tubes, it can become very expensive when other necessary additions are considered. U-tubes, for example, need only one tube sheet and bonnet, resulting in significant cost savings.
Straight tube heat exchanger is vulnerable to the thermal expansion effect. As the tubes heat at varying speeds and pressures, it does not necessarily spread in sync. Since the tubes are attached to these other critical materials, this may cause damage to the tube layer and shell in a straight tube exchanger. This problem can be alleviated with an extension joint, but these additions are not inexpensive. A u-tube heat exchanger, on the other side, is only attached to the tube sheet and shell on one end, allowing for thermal expansion without causing damage to the rest of the system. Tube packets can also be conveniently separated from the exchanger thanks to U-tube designs. This makes it easier to examine and disinfect the shell and exterior of the tube bundle.
Cleaning is another important factor for designers to remember when designing an exchanger. Straight tubes are the simplest to vacuum when there are no twists to contend with. However, some straight tube designs make testing and cleaning of the shell more complicated because the tubes cannot be removed from the shell in some designs.
What is Cross Flow Heat Exchangers and its Working Principles
Summary
This article presented an understanding of what is u-tube heat exchanger, what is the design, what are the advantages. We also compared u-tube heat exchanger and straight heat exchanger. Straight tube heat exchangers are vulnerable to the thermal expansion effect. For more information, you can consult our experts. Please feel free to register at Linquip and get more about u-tube heat exchanger.