What is Drain Valve? Working Principle & Types – A drain valve is a mechanical mechanism that allows surplus liquid or gas to be released from a storage tank, vessel, or container. Although some drain valves are automatically opened when a specific pressure or temperature is met, most drain valves are opened manually by twisting a screw or handle. When the valve is opened, gravity or pressure differential causes liquid or air to drain from the storage tank.
What is A Drain Valve?
A condensate drain valve is a tiny mechanism found at the bottom of the air receiver of a compressor. Whether water flows out of or stays inside the compressor tank depends on whether the air compressor drain valve is open or closed.
While the reservoir tank is the most common location for a drain valve, it may also be used to eliminate moisture from other compressor components and accessories. Compressor filters, drip legs, air dryers, air/water separators, and nearly everywhere else where condensate is a concern can benefit from an air compressor valve extension.
Air may carry a significant amount of water vapor in its natural condition. The function of compressing air diminishes the vapor-holding capacity substantially. Water molecules clump together and generate condensation as a result of compression. Inside the tank, the impact is akin to a thunderstorm.
The critical purpose of a drain valve is to enable surplus water vapor to escape into the atmosphere. The removal of condensation aids in the prevention of corrosion, which can harm the compressor and reduce its lifespan. The drain valve lowers wear on tools and equipment operated by the compressor unit by removing water from the compressed air system.

How Does a Drain Valve Work?
The bulk of industrial air compressors produces between 100 and 175 pounds per square inch of pressure. This pressure enables air compressors to perform an almost infinite number of functions. An air compressor comprises multiple valves that assist regulate the flow of air and pressure to guarantee optimal operation and safety.
To compress air inside a sealed chamber, most industrial air compressors employ one of two methods: pistons or a revolving screw. Naturally, the equipment takes in ambient air around the compressor throughout this operation. Water vapor is present in this air.
When the pressure of air is increased, some moisture in water molecules escapes. In addition, as the air cools to ambient temperature, the water vapor condenses into liquid, releasing more moisture. The water in the tank collects near the bottom. A 200 CFM (25 HP) compressor, for example, will create 18 gallons of water each day.
Water in your compression chamber will quickly cause major issues, including rust and corrosion. Corrosion like this will eat straight through the sidewall of your air receiver if left uncontrolled. Excessive water might also cause the air dryers in your compressor to get overwhelmed and stop working correctly. All of this results in increased wear on tools and other air-operated equipment downstream.
All air compressors feature a drain valve on the bottom of the air receiver to prevent these issues. Water can flow out of the system through the drain valve.
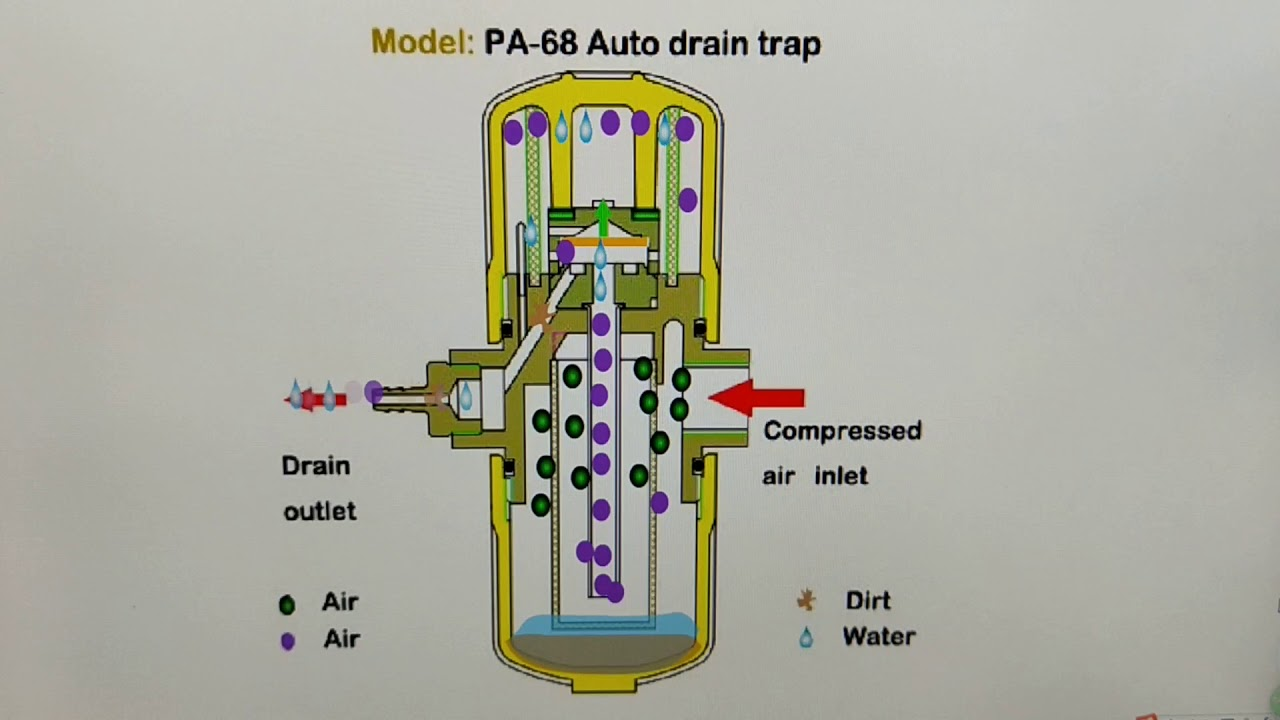
Parts of Drain Valves
A drain valve is made up of a stem and a hollow cylindrical body. The stem runs parallel to the hollow section of the body’s axis. When the stem is open, liquid or gas travels through the hollow area of the body. The stem closes the passage through the body when it is rotated, thereby preventing the liquid or gas from leaving. The stem of certain drain valve designs prevents the flow, whereas the stem of others is employed to raise or lower a flow-blocking gate. Depending on the design, this gate might be in the shape of a disk or a ball.
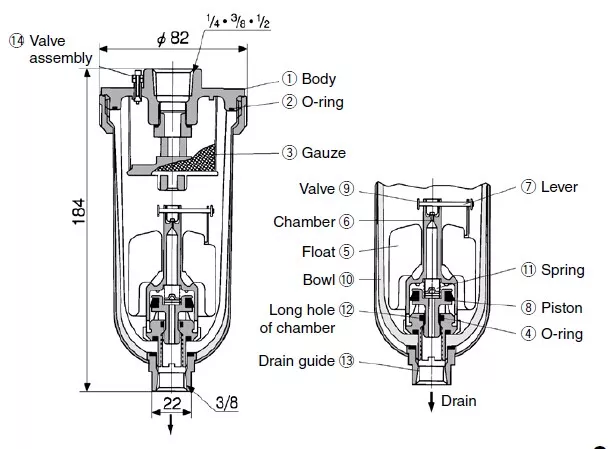
Types of Drain Valves
Drain valves come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from basic screw plugs to automated, electrically controlled types. The most basic oil drain valve on a car is a threaded plug placed into a matching threaded hole in the engine oil pan. The plug serves as the valve stem, and it is activated by removing it from the oil pan. Highly complicated valves, on the other hand, are electronically controlled to open at certain periods or in reaction to a predetermined temperature or pressure thresholds.
A manual drain valve is the most basic sort of drain valve. It remains closed unless manually opened by a person. The operator is responsible for emptying the condensate from the tank on a regular basis. This task should not be too difficult for smaller air compressors.
For industrial air compressors, a manual drain valve isn’t practicable. Instead, one of three valve types is used in such air compressors.
A float-operated drain, for example, is made of a unique housing constructed around the drain valve. Water pours into this housing as it accumulates in the tank. A float inside the housing rises as the water level rises. When the float reaches a predetermined level, the drain opens and the water flows out. With this sort of valve, some compressed air is wasted. This can waste power in bigger air compressor systems.
A timer-controlled drain, the second type of drain valve, utilizes a different strategy. The water level is not measured by the valve. Instead, an electrical timer is used to open and stop the valve at the user’s specified timings. The amount of liquid generated fluctuates because the water in compressed air depends on the ambient relative humidity. Again, compressed air and energy might be lost.
A zero-loss drain, the third type of drain valve, has a distinct triggering mechanism. The presence of water in the valve is monitored by a sensor probe. When the water level rises to a certain level, the probe transmits an electrical signal to a solenoid, which opens the drain but stops the flow before any compressed air is released.
For air compressors used in highly controlled environments, a timed valve makes sense. The valve may be configured to open at certain periods after the water accumulation rate has been calculated. This balances drainage against the air loss that might happen when a drain valve opens.
Application of Drain Valves
Drain valves are utilized in many different situations. They’re common in things like air compressors and air supply lines. An air drain valve allows potentially dangerous condensates like water, oil, or rust to be removed. These impurities can accumulate over time, obstructing the airline or weakening the storage tank. The interior of steel storage tanks might corrode if there is too much water in the system. On big vehicles with air braking systems, automatic air drain valves are often utilized to remove oil and water that may cause the brakes to fail.
Water heater drain valves are used to drain water and remove contaminants from hot water heaters on a regular basis. Mineral scale, composed of calcium or other minerals, can build up within water heaters over time. Sediments such as dirt or sand can also accumulate in the tank’s bottom. If left unchecked, this reduces the heating efficacy of the heating components and can eventually lead to irreversible damage. Most of these contaminants may be drained from the hot water heater by periodically opening the drain valve.

How to Use a Drain Valve
Each drain valve type described above is self-contained, requiring little or no physical intervention. The most difficult part is deciding on a model that is compatible with your equipment and fits your operational needs.
If your compressor is not near an electrical supply, for example, a float-operated machine makes sense. If you use your compressor on a regular basis, a timer-controlled model is probably the best option. If you’re concerned about compressed air loss while draining, a zero-loss air compressor drain valve is ideal.
Do you need assistance choosing a drain valve? Inquire about it at the Linquip platform! There you can find numerous Manufacturers and Distributors of valves along with various Service Providers.
FAQs about Drain Valves
1. What is the purpose of draining valves?
The critical purpose of a drain valve is to enable surplus water vapor to escape into the atmosphere. The removal of condensation aids in the prevention of corrosion, which can harm the compressor and reduce its lifespan.
2. Should the drain valve be open or closed?
If the unit will not be used for a long time, it is advisable to keep the drain valve open until it is needed. This allows moisture to drain entirely and prevents rusting on the interior of the tank.
3. Where should drain valves be installed?
Above the internal stop valve, a drain-off valve must be fitted. It is the property owner’s obligation. The building water service is made up of the communication and supply pipes.
4. Which way do you turn a drain valve?
To open the drain, look at the handle of the drain valve and turn it counterclockwise. Close the drain by turning it clockwise. It’s common for new valves to be difficult to turn. If necessary, use pliers; the valve will not be damaged.
5. Why is the drain valve used in air bottles?
To remove collected condensate from the receiver, a drain valve is installed at the bottom of the bottle.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Provider
Read More In Linquip
- How to Prevent Sewer Backflow Valve Problems?
- What is Pilot Valve? Working Principle & Types (Complete Guide)
- What is Poppet Valve? Working Principle, Types & PDF
- 6 Different Shower Valve Types + Pictures: Your 101 Guide!
- The 9 Best Ball Valves: Top Rated Models (2022 Reviews)
- 6 Parts of Butterfly Valve + Function: A complete guide!
- Types of Pressure Relief Valve: All you need to know about PRVs
- 6 Main Types of Plumbing Valves: Complete Guide
- Air Release Valve Installation Costs in 2022 (Ultimate Guide) + PDF
- Angle Valve Installation Costs: Practical Factors in 2022
- Globe Valve Installation Costs in 2022 (Clear Guide) + PDF
- Gate Valve Installation Costs and Maintenance in 2022 (Clear Guide)
- 6 Main Types of Expansion Valves: an Easy to Understand Guide
- Angle Valve: The Most Essential Tips of Features, Functions & Applications
- Globe valve parts 101: All you need to know in one place
- The 10 Best Sprinkler Valves in 2022
- What is Automatic Expansion Valve: A Basic Guide



