Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a nutshell 2022
Paper Capacitor – Resistors and capacitors are utilized as passive components in every electronic circuit to resist and store electrical energy. In general, a condenser is a paper capacitor that consists of two conducting surfaces separated by an insulating substance. The dielectric is the name given to this substance.
From one circuit to another, capacitors provide a low resistance channel to A.C voltage and a high resistance path to D.C voltage. The circuit’s capacitance is saved in the form of an electric field. It obstructs the flow of direct current and opposes the flow of voltage in any electrical circuit. Capacitors come in a variety of packaging, types, and values, depending on the application.
What is a Paper Capacitor?
A paper capacitor is a capacitor that is created with paper as the dielectric medium and is capable of storing the electric charge in it. These are the capacitors that prefer to store fixed amounts of charge value. As a result, these capacitors are classified as fixed-type capacitors. The dielectric is bathed in wax or oil to protect it from the impacts of the environment. These capacitors have a set capacitance value.
The Function of a Paper Capacitor
A paper capacitor consists of two metallic plates separated by a dielectric substance such as paper. It consists of both positive and negative plates. When a small quantity of electric charge is supplied to the plates, one plate attracts a positive charge while the other attracts a negative charge. The electrical field is used to store this electrical energy. The discharge of a capacitor uses this stored electrical energy. These come in sizes ranging from 500pF to 50nF. These have a lot of leakage current.
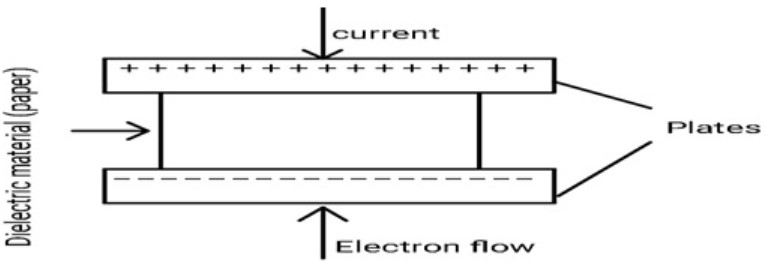
Construction of a Paper Capacitor
This sort of capacitor has a straightforward design. It is determined by the sheet of paper selected. As a result, these are divided into two groups based on their construction. They are as follows:
- Paper Sheet
- Metalized Paper
Paper Sheet Type Capacitor
Two metal sheets and a paper sheet are required for the fabrication of the paper sheet capacitor. The paper sheet is waxed or drenched in oil to protect it from the outer environment. Paper capacitors are fixed capacitors with a fixed capacitance value that hold a fixed amount of electric charge. The dielectric medium is the paper sheet sandwiched between the metal sheets, while the aluminum functions as an electrode.
Because paper is a poor conductor of electricity, it prevents electric current from flowing between the aluminum sheets, allowing the electric field to pass through and acting as an electric current barrier. To protect it from moisture in the air, the paper sheets and two metal sheets are rolled into a cylindrical shape and covered with wax or plastic resin. The ends of the two metal sheets are used to make the two-wire leads.
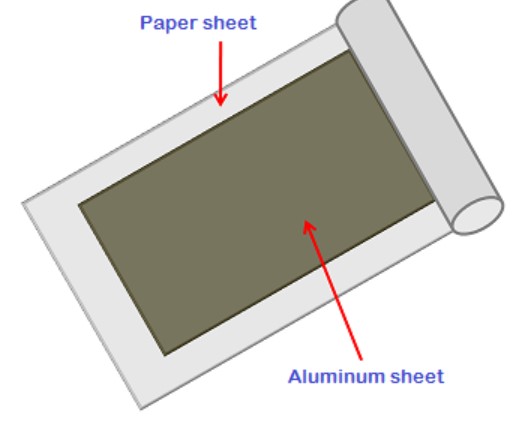
Metalized Paper Capacitor
The paper is coated with a thin layer of zinc or aluminum and rolled into a cylinder in a metalized paper capacitor. To protect it from the elements, the entire cylinder is wax-coated. The electrodes are made of metalized paper, and the paper serves as a dielectric medium. Due to chemical activity, this type of zinc-coated capacitor is readily damaged. As a result, aluminum is widely used in the construction industry. When compared to the paper sheet capacitor size, the metalized paper capacitor is very tiny. When compared to the aluminum utilized in the paper sheet capacitor, it has a very thin layer of metal.
The Structure and Characteristics of Paper Capacitors
Paper capacitors are composed of shell packaging or epoxy resin potting and use specific capacitor paper as the medium, tin foil or aluminum foil as the electrode, and are coiled into a cylindrical shape before connecting the lead and passing the staining process. The figure depicts its structure.
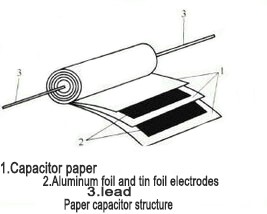
Paper capacitors have the following characteristics:
- The capacitor paper may be wound into a large-capacity and small-volume capacitor with a capacitance of 1-20F due to its tiny dielectric thickness (usually only 6-20μm) and high tensile strength.
- The capacitance range is wide, and the working voltage is high.
- Lacks chemical and thermal stability, making it susceptible to aging.
- There is a significant dielectric loss.
- The working temperature is usually between 85°C and 100°C.
- Because it is hygroscopic and requires sealing, it is not suited for use in high-frequency circuits.
- Low production costs and a simple technique.
- Paper capacitors are typically utilized in low-frequency and DC circuits.
Working of a Paper Capacitor
A capacitor with a fixed capacitance value is known as a fixed capacitance capacitor. Because there is no electrolyte in this sort of capacitor, it operates as a generic parallel plate capacitor.
Capacitor Values
The following steps can be used to determine the value of this capacitor:
- The symbol on the capacitor represents the capacitance in pico-farads of the specific capacitor.
- If the third represented number in a three-digit number is ‘0′, The value then represents P.
- When a three-digit number is printed, the third digit signifies the number of zeroes.
Color labeling is used on some capacitors. Capacitor values and kinds are determined as a result of this. The size of a paper capacitor varies from 300 picofarads to 4 microfarads. Its operational voltage rarely reaches 600 volts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantage of a paper capacitor is that it has a set capacitance value. During the manufacturing process, the capacitance value is fixed.
The biggest downside is that it collects moisture from the air, lowering the dielectric’s insulating resistance. The dielectric medium is modified as it collects moisture from the air.
Applications
Paper capacitors can be used in a variety of ways. Here are a few examples:
- This is applicable to a wide range of electrical and electronic applications.
- This can be used for filtering purposes.
- These are utilized in applications that need a lot of voltage.
- These capacitors are utilized in high-current applications.
FAQs
1). What is the Paper Capacitor Used for?
An electronic device that stores electrical energy in the form of an electric field is known as a paper capacitor. It’s applied in a wide range of high-voltage, high-current applications.
2). What is the Symbol of a Capacitor?
A capacitor is a passive electrical element that stores electric charges in the form of an electric field. Farads are used to measure capacitance. When a capacitor’s capacitance is higher, it can store more electric charges.
3). What Metal is used in Capacitors?
The capacitor’s plates are made of metals that conduct electricity, such as aluminum, tantalum, silver, and other metals. Depending on the application, the dielectric media is formed from insulating materials such as paper, glass, ceramic, rubber, or plastic.
4). What are the types of Capacitors?
There are five different types of capacitors. They are,
- Film capacitors
- Paper capacitors
- Ceramic capacitors
- Electrolytic capacitors.
- Dielectric capacitors
5). How Do You Know if a Capacitor is Good?
To determine the capacitor’s quality, all we need is a digital multimeter with a wide range and any sort of capacitor found in a device.
Connect the multimeter leads to the capacitor plates’ two ends. Connect the multimeter’s red lead to the capacitor’s positive plate and the black lead to the negative plate. The capacitor is good if the meter reading starts at zero and gradually increases to infinity.
The capacitor can thus be examined with a digital and analog multimeter to determine whether it is good, bad, open, or short.
How to Select an Appropriate Capacitor?
Introduction
Capacitors come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they’re used in a wide range of applications in electronics. When choosing a capacitor, consider the type of construction, tolerance, working voltage, and temperature coefficients, even if they all perform the same basic function. This section will show you how to choose the proper capacitor for any circuit.
Value
From 1pF to 100,000mF, capacitors are available. Depending on the type of capacitor, not all values are possible.
Working Voltage
Always utilize a capacitor with a higher working voltage than the circuit in which it is applied. This is especially important in high-value electrolytic capacitor power supply systems. The working voltage should always be at least 20% higher than the circuit’s max working voltage.
Polarisation
Polarized capacitors contain distinct positive and negative terminals. They must never be utilized in a circuit where the voltage could reverse polarity or be wired the incorrect way around. If electrolytes are connected incorrectly, they may explode.
Tolerance
A high-precision capacitor may be required in some circuits, such as timing or oscillators. The circuit may not deliver the required results or may not operate if the capacitor utilized does not have the same tolerance as indicated in the parts list.
Temperature Coefficient
This is the change in capacitance as a function of temperature. Temperature fluctuation in parts per million per degree Celsius, also known as Tempco, can be stated as a percentage or as a change in parts per million per degree Celsius. Capacitors can have positive or negative temperature coefficients, meaning their value rises or falls as the temperature rises or falls (Negative Positive Offset). In radio and tuned circuits, NPO capacitors are frequently utilized.
Leakage Current
A leakage current runs across the dielectric in some capacitors, causing them to lose their charge. Low-leakage capacitors, such as Tantalum Bead, are available and are used in applications such as timing circuits.
Polyester
Polyester capacitors are available in a range of capacitances from 1nF to 15uF. Sometimes they’re packaged in color bands that match the resistor color code (left), and other times they’re just plain (right). Working voltages range from 50V to 1500V, and tolerances of 5%, 10%, and 15% are offered. Decoupling circuits frequently use this material.
Polycarbonate
These capacitors are obtainable in sizes ranging from 100pF to 10uF, with operating voltages up to 400V and tolerances of 5% or 10%. They have a temperature coefficient of roughly 100 parts per million per degree Celsius. Filtering and timing circuits frequently use this material.
Ceramic Disc
Ceramic discs are offered in a wide range of tolerances, from 1pF to 220nF, with operating voltages up to 100V. They’re used for a variety of things, including decoupling circuits, and they have a lot of capacitances for their size.
Electrolytic
Electrolytic capacitors range in size from 1uF to 47000uF, with operating voltages up to 600V and extensive tolerance ranges. They’re widely employed in power supply, audio amplifiers, and decoupling applications. If you don’t connect with the correct polarity, gas will build, and the casing will explode.
Variable and Trimmer
Radio circuits, RF oscillators, and transmitters all make heavy use of variable capacitors. They are frequently available in single gang or multi-gang configurations and range from 25p to 1000pF. The trimmer capacitor is the smaller sibling, and once set, it cannot be changed. Trimmers are available in various sizes, ranging from 5p to 100pF.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip
- Types of Capacitors: All You Need to Know
- Difference between Capacitor and Inductor- Capacitor vs. Inductor
- What is a Non-Polarized Capacitor? Types & Function
- What is Mica Capacitor Used for?
- What is Paper Capacitor Used for?
- Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a nutshell 2022
- What is Capacitor and How it Works
- 7 Types of Capacitors and Their
- What is Ceramic Capacitor Used for
- What are Mica Capacitors? Comprehensive Overview
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor
- What is Polarized Capacitor? Function and Applications
- What is Film Capacitor & What is it used for
- What is Film Capacitor? Different Types & Working
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor? Usage & Application
- What is Ceramic Capacitor? A Basic Description
- What is Capacitor Start Induction Motor: A Complete Guide



