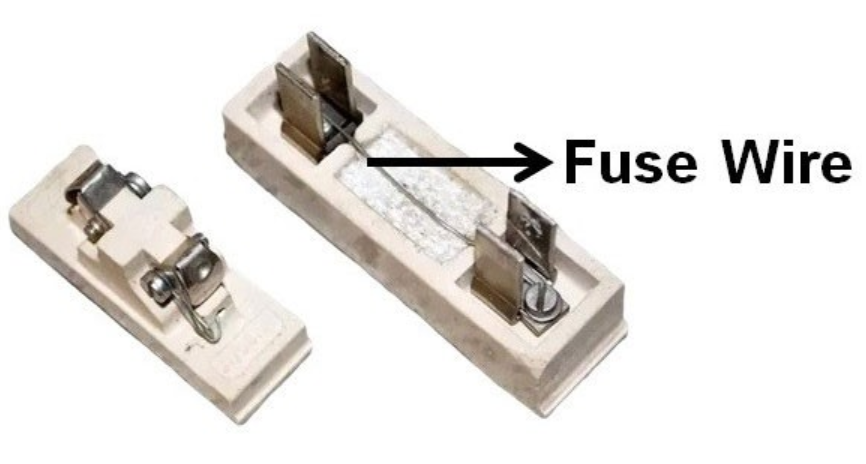
What is a Fuse Wire – A fuse wire is a safety wire that is linked in series with the live wire; in the event of an electrical fault or excessive current supply, the fuse wire melts and interrupts the electrical circuit.
On the Linquip website, among the many options available to you, you will find all the information you need to know about Fuse, as well as information regarding this marketplace. You can count on Linquip to provide you with as much general and reliable information about this topic, whether you’re a professional or a customer looking for a proper company. We recommend you review a list of all Fuses for Sale available in Linquip.
We would be delighted to provide you with more information on how we can help you generate revenue within your industry. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions! With Linquip’s Solutions for Each Company Level, you will be able to upgrade the capabilities of your organization in order to gain a competitive edge by taking advantage of a wide range of options to enhance your organization’s performance. If you are looking for the simplest or the most sophisticated marketing and advertising package for your business, we can help you ensure that your company gets as many customers as possible to grow your business.
What is a Fuse?
An electrical fuse protects an electrical circuit against damage caused by overcurrent in electronics and electrical engineering. The primary component of the device is a strip or metal wire that melts when too much current moves through it, stopping or interrupting the current. A fuse is a sacrificed device; once it blows, the circuit is open and needs to be repaired or rewired, depending on the fuse’s kind.
Since the beginning of electrical engineering, fuses have been utilized as crucial safety equipment. Depending on the application, there are hundreds of different fuse designs with varied current and voltage ratings, breaking capacities, and reaction times. Fuses are chosen based on their time and present working characteristics in order to offer enough protection without unneeded disruption. For certain circuits, wiring standards often specify the maximum fuse current rating. The main causes of fuse operation are device failure, overloading, mismatched loads, and short circuits. A short circuit will occur and the fuse will melt if a broken live wire comes into touch with a grounded metal casing.
A fuse is a device that automatically cuts power to a malfunctioning system; it is sometimes abbreviated as ADS (Automatic Disconnection of Supply). Fuse replacement options include circuit breakers, however they differ greatly in many ways.

Construction of an Electrical Fuse
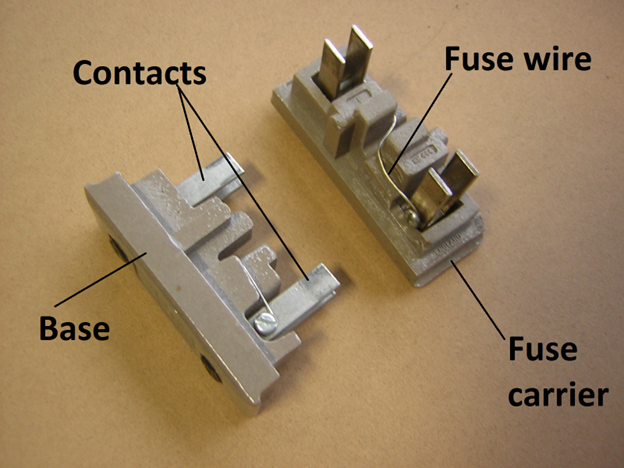
A fuse is made out of a small-cross-section metal strip or wire fuse element that is positioned between two electrical terminals and (typically) protected by a non-combustible housing. The fuse is set up in series to handle all the current flowing through the circuit that is being protected. Due to the current flow, the element’s resistance produces heat. In order to prevent the element from overheating due to the heat generated by a typical current, the element’s size and construction are (empirically) chosen. If the current is too high, the element heats up to a greater temperature, melts, or melts a soldered junction within the fuse, which opens the circuit.
Zinc, copper, silver, aluminum, or alloys of these metals or other metals are used to create the fuse element in order to give stable and predictable features. In a perfect world, the fuse would swiftly melt on a minor excess current while carrying its rated current indefinitely. The element must neither oxidize nor change its behavior after perhaps years of use, nor must it be harmed by small, innocuous surges of current.
The form of the fuse components can alter their ability to heat up. The current may be split across several metal strips in big fuses. A dual-element fuse may have a metal strip that melts immediately in the event of a short circuit and a low-melting solder junction that reacts to a prolonged overload of low values as opposed to a short circuit. Steel or nichrome wires can support fuse elements so that they are not put under stress, but spring can be added to speed up how quickly the fuse element fragments separately.
The materials used to expedite the quenching of the arc or air may surround the fuse element. You might use non-conducting liquids or silica sand.
FAQs about Fuse Wire
1. Where Is The Fuse Wire Used?
Electric circuits employ fuse wires to stop extra electricity from entering the circuit, preventing harm to the equipment.
2. What Is A Fuse Wire Made Of?
A tin and lead alloy is used to make the most common type of fuse wire.
3. What Is The Function Of A Fuse Wire?
A fuse is a safety device used in electrical circuits to prevent damage from an overcurrent. A metal wire or strip that melts when an excessive current travels through it is a crucial part of an electrical fuse.
Download What is a Fuse Wire PDF
You can download the PDF format of this post from here.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Types of Electrical Wire + Application (Complete Guide)
- Circuit Breaker vs Fuse- What are the Main Differences?
- Solid vs Stranded Wire (A Practical Guide)
- What Is CNC Machining & How Does It Work? (A Comprehensive Guide)
- What is Electrical Identification? (2022 Ultimate Guide)
- What is a Paper Capacitor?
- What is Synchroscope? Method & Working Principles
- What is Non-Polarized Capacitor? Definition & Usage
- Top 10 Machine Shops in Tampa in 2022 (Clear Guide)
- 10 Types of Molding Machinery + PDF (Clear Guide)
- 3 Common Types of Electrical Connectors (Clear Guide)
- Types of Sensors Detectors/Transducers: An Entire Guide