In this article, after having a very short description of DC motors, you will read about their different types of design very specifically and then their parts, components and structures. Then we move on to explain the uses and applications of a DC motor in different scales. The last thing we will discuss is their advantages and disadvantages to assist you to have a better choice. So, let’s learn about the construction of the DC motor and its parts with Linquip. But first about Motor :
⇒ View a List of DC Motors for Sale and Their Suppliers ⇐
Interested in learning about the Functions of a DC Motor? A DC Motor’s functioning principle and uses may be found here at Linquip. In search of a place to purchase DC motor Equipment? Visit Linquip’s DC Motor For Sale, where you can see a complete list of all DC Motor Products depending on your needs and application.
For your convenience, Linquip also provides a list of DC Motor Suppliers and Companies from which you may select the best one. Linquip has a wide variety of DC Motor Manufacturers who can help you discover the right equipment for your application. The best DC Motor Service Provider businesses can also manage your industrial equipment service activities, such as the installation, maintenance, and repair of your industrial equipment.
What is a DC motor?
DC motors are devices designed to convert direct current electrical energy to mechanical energy! This rotary electrical device has different types, all of them containing either electronic internal mechanism or electromechanical internal mechanism responsible for changing the direction of current in the motor.
Different types of DC motor designs
Some of the most popular designs for DC motors are Permanent magnet, Brushless, Shunt, Series, and Compound wound or stabilized shunt. The DC motor parts are normally the same within these different designs and the overall operation is similar. How it operates is that a conductor, carrying the current is implanted in a magnetic field, and the power applied through the conductors enables the rotation of the motor. The generation of electromagnetic fields and its place, whether in the rotor or stator is the reason these designs differ from each other. As getting acquainted and understanding the diverse types of direct current motors will aid you to figure out how they are used for different applications and which one is more suitable for your application, in what follows, we will elaborate the function of some of these types.
- Permanent Magnet Motors
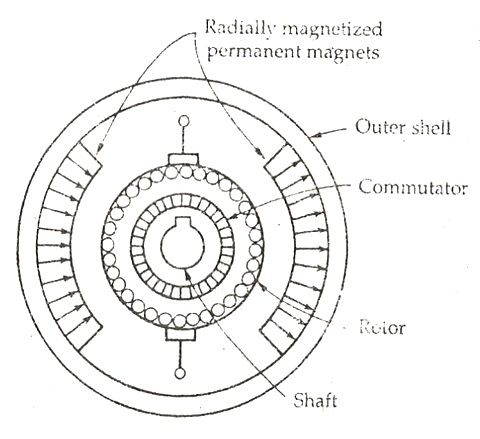
Permanent Magnet Motors (also known as a PMDC motor) apply a permanent magnet to make a field flux. This type of DC motors creates a great starting torque with a good speed regulation. With limited torque it has, permanent magnet type typically is used on low horsepower applications. - Shunt Motors
the field of shunt type is connected in parallel with the armature windings. As the shunt field can excited separately from the armature windings, this type of motors provides a great speed regulation. Besides, shunt motors also offer simplified reversing controls. Zenegra 100 mg http://www.wolfesimonmedicalassociates.com/zenegra/ - Series Motors
A series DC motor consists of a field wound with some turns of a wire which carries the current of armature. Like permanent motors, series motors create a large amount of starting torque. In comparison with permanent motors, series type can’t regulate speed. In addition, if series motors run with no load, they can be damaged. These limitations make series motors unsuitable for variable speed drive applications. - Compound Motors
Like shunt DC motors, compound motors possess a shunt field which is separately excited. Just like permanent and series motors, compound motors enjoy good starting torque with some problems in speed regulation in variable speed drive applications.
These four main types of DC motors have the numerous potential applications Each type of these motors possesses its strengths and weaknesses. As mention in the beginning of this section, getting acquainted with different types can assist you figure out which type is more suitable for your applications.
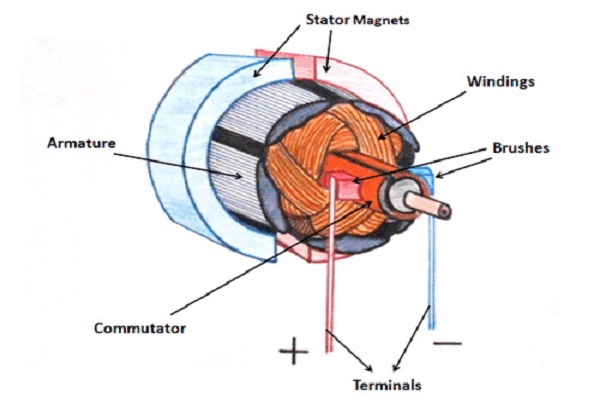
What are DC Motor Parts and how they work?
8 Parts of DC Motor are:
- Stator
- Rotor
- Yoke
- Poles
- Field Windings
- Armature Windings
- DC Motor Commutator
- Brushes
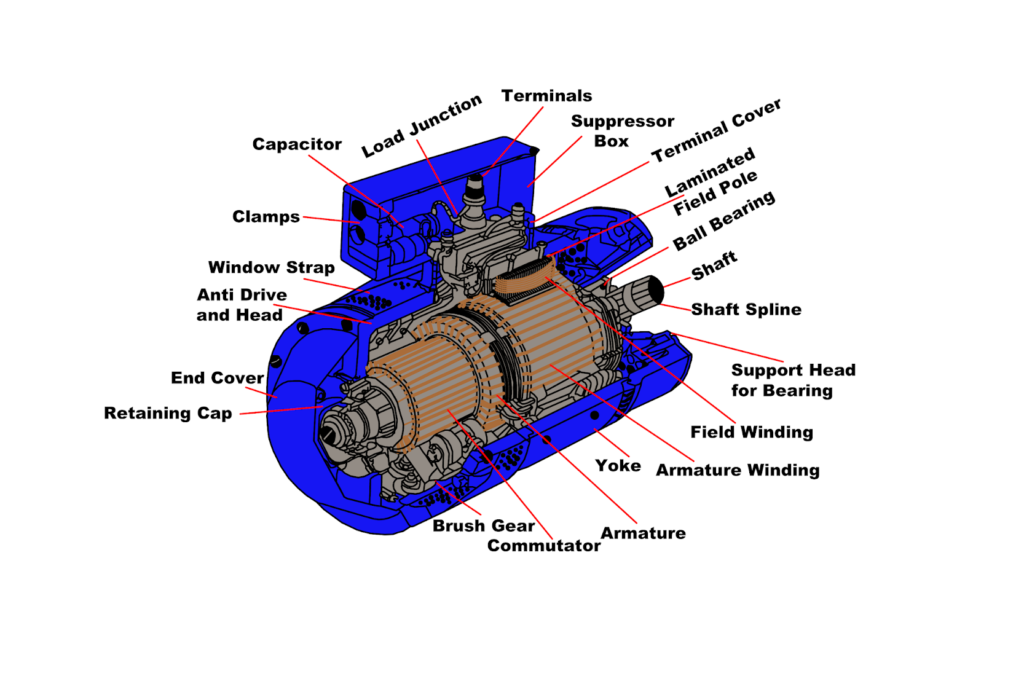
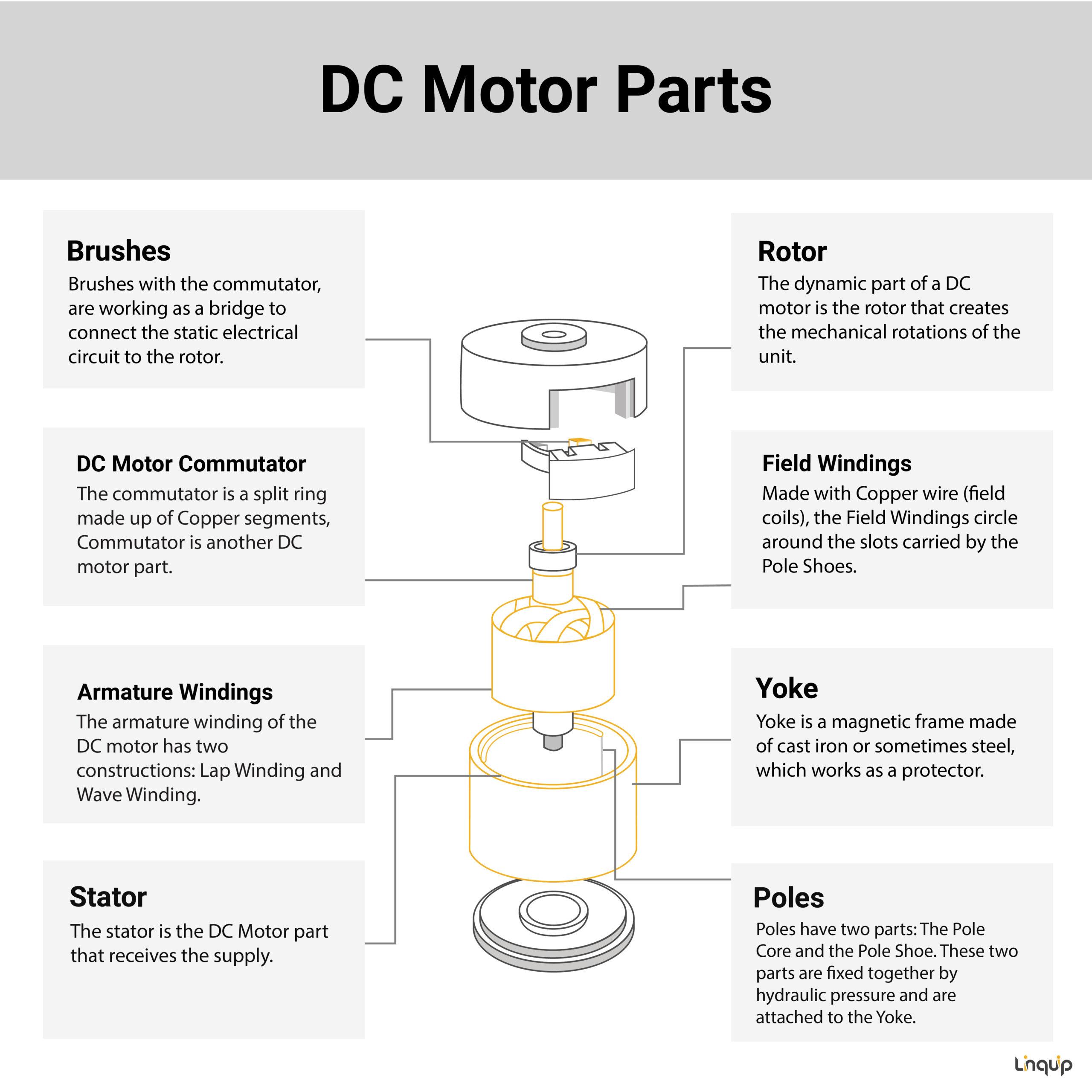
A DC motor contains different parts that understanding each one can assist to know deeply these parts cooperate with each other and in the end how DCs work. These components are: a stator, a rotor, a yoke, poles, armature windings, field windings, commutator, and brushes. Many of its parts are the same as parts of AC motor, but with a little change.
1. Stator
A stator is one of the DC motor parts that is, as the name suggests, a static unit containing the field windings. The stator is the DC Motor part that receives the supply.
2. Rotor
The dynamic part of a DC motor is the rotor that creates the mechanical rotations of the unit.
3. Yoke
Another unit of the DC motor parts is the Yoke. A Yoke is a magnetic frame made of cast iron or sometimes steel, which works as a protector. This protective cover keeps the inner parts of the motor safe and sound and also supports the armature. Yoke also houses the magnetic poles and field windings of a DC motor to help supporting the field system.
4. Poles
DC motor has magnetic poles that fit into the inner wall of the Yoke with the help of screws to tighten them up. Poles have two parts: The Pole Core and the Pole Shoe. These two parts are fixed together by hydraulic pressure and are attached to the Yoke. Each part of the Poles has a specific task based on its design. The core holds the Pole Shoe over the Yoke while the Pole Shoe is structured to both carry slots for the field winding and spread the produced flux by the field windings into the air gap between the rotor and stator. It helps to reduce the loss caused by reluctance. Phentermine diet pills http://www.024pharma.com/phentermine.html
5. Field Windings
Made with Copper wire (field coils), the Field Windings circle around the slots carried by the Pole Shoes. The field windings form an electromagnet capable of producing field flux. The rotor armature rotates inside the field flux, resulting in the effective flux cutting.
6. Armature Windings
Another DC motor parts is armature winding. The armature winding of the DC motor has two constructions: Lap Winding and Wave Winding. Their difference is in the number of parallel paths. Armature Winding is attached to the rotor and alters the magnetic field in the path that it rotates. The result of this procedure is magnetic losses. Designers try to reduce the magnetic losses by making the armature core with some low-hysteresis silicon steel lamination. Then, the laminated steel sheets will be piled up together, creating the cylindrical structure of the armature core. There are slots designed inside the armature core with the same material.
7. DC Motor Commutator
The commutator is a split ring made up of Copper segments, Commutator is another DC motor part. The operating system of a DCs is based on the interaction of the two magnetic fields of rotating armature and a fixed stator. As the north pole of the armature is attracted to the south pole of the stator and south pole of armature is attracted to the north pole of the stator, a force is produced on the armature which makes it to turn. the process in which the field in the armature windings is switched to produce constant torque in one direction is called Commutation. the commutator is a device connected to the armature enabling this switching of current. Different segments of its cylindrical structure are insulated from each other by Mica. The commutator is designed to commute the supply current to the armature winding from the mains. The commutator passes through the brushes of the DC motor.
The basic purpose of commutation is to certify that the torque acting on the armature is always in the same direction. Naturally, the generated voltage in the armature is alternating, the commutator converts it to the direct current. To control the direction the electromagnetic fields are pointing to, the commutator turns the coils on and off. On one side of the coil, the electricity should always flow away, and on the other side, electricity should always flow towards. This ensures that the torque is always produced in the same direction.
8. Brushes
The last item on the DC motor parts list is Brushes that are made of Carbon or Graphite structures. Brushes with the commutator, are working as a bridge to connect the static electrical circuit to the rotor. Brushes are in contact with the commutator and relay the produced current to the commutator from an external circuit. The current then moves into the armature winding.
What is the Mechanism Through Which a DC Motor Generates Torque?
A rotating magnetic field can be created by sequentially turning on and off coils. There are a number of moving magnets (permanent or electromagnets) that interact with these revolving magnetic fields to produce a torque on the armature, which causes it to revolve.
Applications of DC Motors
Due to the fact that there are 4 main types of DCs, a wide range of different applications is defined for DC motors. The previous sections considered some of the various parts and types of DCs. In this section, we are going to introduce different applications and circumstances where DC motors are used for.
Generally, because of some specific advantages of each type of DC motors, there are various uses of them. At home, small ones are used in tools, toys and many household appliances. Some other applications of DCs include conveyors and turntables and in industries, huge DCs usages consist of braking and reversing applications. We tried to bring some specific examples as the DCs applications:
-
Pumps
Hydraulic pumps as an essential industrial tool are used in almost all industries such as construction, mining, manufacturing and steel. DC motors because of their variable speed control and also excellent starting torque are used to empower these kinds of pumps. Most of the time lower-cost brushless DCs are used in pumps which make it far easier to maintain on such a large industrial scope.
-
Toys
Due to the fact that small DC motors are easy to use and considerably rugged, they are the best choice of manufacturer and hobbyists for children’s toys such as remote-control cars and trains. Toys that require different range of speed and types of movements need a motor with a wide variety of voltages. Manufacturers find all of these specifications in DCs.
-
Electric Cars
Another application for DCs is in electric cars. DC motors because of their energy efficiency and durability are one of most favorite options for electric vehicles. Moreover, many hobbyist use DCs because of their great and higher starting torque particularly series-wound motors, and their variable speeds with voltage input.
-
Robots
For many hobbyist and engineering robots are any electromechanical devices designed to do one or more specific tasks. To activate things like tracks, arm or cameras, DC motors are one of the most achievable and reasonable choices with lower costs. The specifics like high torque and durability and also efficiency make DCs ideally suitable for robotics.
DC motor Advantages and Disadvantages
Different sizes of DC motor parts will create different DC motors, suitable for different needs. As mentioned before, small ones can be used in toys, tools, and home appliances and larger ones are used in the elevator and hoists and propulsion of electric vehicles. Although AC motors decreased the selling of DC motors on account of simple generation and transmission with fewer losses to long distances, needing less maintenance and can be operated in explosive atmospheres, DCs still are utilized in where ACs can’t fulfill the needs. DCs have their own unique features and importance in industries that make up for lots of other advantages that AC motors have over them.
DC motors are suitable for low-speed torque, or when having an adjustable speed and constant is necessary. In other words, with DC motors the speed can be controlled over a wide range. This means they offer a wide range of speed control both below and above the rated speed. This feature of DC motors can be got in shunt types. By armature controlling and field controlling, you can enjoy this unique advantage of DC motors over AC motors. Moreover, DCs have a very high and strong starting torque compared to normal operating torque. Therefore, DCs are used in electric trains and cranes having overwhelming burdens in the beginning conditions. In addition to the above-mentioned advantages, DC motors have smaller converters and drives as well as higher motor power density. Not to mention that they have full torque at zero speed!
Being around on the market for more than 140 years, DC motors are often more affordable than AC motors and have a simpler and more efficient design. Plus, their maintenance is easy and takes little to no time. If you redesign your current installation to use an AC motor, it will cost way more than just simply replacing the DC motor inside the installation. So, you not only repair your system by installing a new unit inside but save lots of money. Needless to say that such small replacement saves time as well and happens quickly without wasting your time. Need more advantages to fall in love with DC motor parts and structure?
Now that you’ve reached here you know DC motor parts and functions based on the information that Linquip provided for you in this article. Share your comments with us in the comment section and let us know your thoughts and questions while reading this article. Need to find the answer to your questions quickly and troubleshoot your DC motor part? Sign Up on our website and an expert will be there for you.
Download DC Motor Parts PDF
For a better understanding of the basics of DC Motors, their working principle, and types look at this PDF that can help you better understand DC Motors.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- What are the Advantages of DC over AC?
- What is the Working Principle of DC Generator?
- A Simple Guide to the Difference Between Motor and Generator
- Difference between AC and DC generators: An easy to understand guide
- What is AC Motor? Types, Principles and Constructions
- What are the parts of AC Generators?
- DC Motor Efficiency
- Your Guide To The Working Principle Of DC Motor
- All About DC Motor Types and Their Applications
- The Good Guide to Types of Electric Motors
- Types of Generators: Learn the Basics, Get the Most Out f it!
- DC Motor Working Principles : The Most Compendious Reference
- A complete Guide to The Difference Between Stepper Motor and DC Motor
- Parts of DC Generator: Explanation of Parts, Working, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages
- Diesel Generator Parts: A Complete Description
- What are The Electric Generator Parts?





I was an industrial, AC-DC stator-armature winder, for National Electric Coil, McGraw-Edison Service, and Cooper Industries, in the 70s and 80s. One particular wound rotor, that I rewound, had 4 windings. First, in the laminated slot, a 3ph. machine wound, poly coated, multi turn, group of coils, connected to three slip rings. I do not recall, whether wye or delta connected. Next, a machine form wound, machine spread, 3 or 4 conductor frog leg, one turn, group of coils, connected to a commutator, on the opposite shaft end, of the slip rings. Next, a group of hand formed, single poly coated equalizer coils, installed around the commutator mica V-ring, connected to the commutator riser slots. Last a 3 or 4 poly coated, 2 or 3 turn, hand wound group of coils, connected into commutator risers. CAN you please explain what type of motor-generator this was. Also how it may have been used in Industry. I wish, that I could recall the Customer’s name. THANKS, TIM MARQUARDT
Thank you for your review and for bringing this to our attention. We couldn’t agree more. Please sign up on Linquip to share your question or suggestions with our experts. Again, thank you for taking the time to review our article!
Wow, without seeing a diagram for sure hard to say. Several configurations come to mind.
1/ it’s an amplidyne, a configuration used for mainly position control, like gun turrets, they were coined the “short circuit that does work “, because of the larger gauge small turn windings. High precision early military equipment.
2/A dynamometer, a dc driven machine mainly for aircraft, dc driven by batteries or on board APU to generate 3 phase @ 400 hz for navigation avionics, 400 hz is used because at that frequency transformers etc have much less iron ( lighter for planes)
3/ lastly an early cycloconverter , either ac or dc driven with the resulting output opposite what you are putting in, like a universal dynamo.
i hate this thing i hate school i just want to go home and watch you tube
I am just in the process of gathering info on a small home pilot project searching for a suitable DC motor for my pet application project. I need support on electrical and mechanical equipment and motors so i am here to learn.
Thank you for visiting our website, Jeyapal! You can communicate with our experts, who can help you solve your issue with finding a suitable DC motor for your project.
I have surveyed other online correspondences but Linquip motors appear to attract my capital outlay for this project. Thanks
Thank you very much Jeyapal for visiting our website, and also thanks for your great comment! We also encourage you to visit other blog posts of Linquip website for more information about motors. You can also visit our Motor Products page, where you can find numerous motor models and brands.
Thankyou for this article.
Thanks for visiting our website, Tim! You can visit our Industrial Equipment page, where you can find various pumps based on your application and demand. You can also visit our expert page and take advice from hundreds of professionals on your issue.
Good morning, I’m Kalio Kaizer Tamunokonbia from Nigeria. I really love your the articles on your website.
Please I need a help from you. How can I produce Electricity at home using DC motor, AC motor, Alternator, armature,1 with flywheel 2, without flywheel. In PDF with full specifications and names of all the materials used. Diagram showing detailed connections. Thank you
Thanks for visiting our website, Kalio! You can visit our Industrial Equipment page, where you can find various DC Motors on your application and demand. You can also visit our expert page and take advice from hundreds of professionals on your issue.