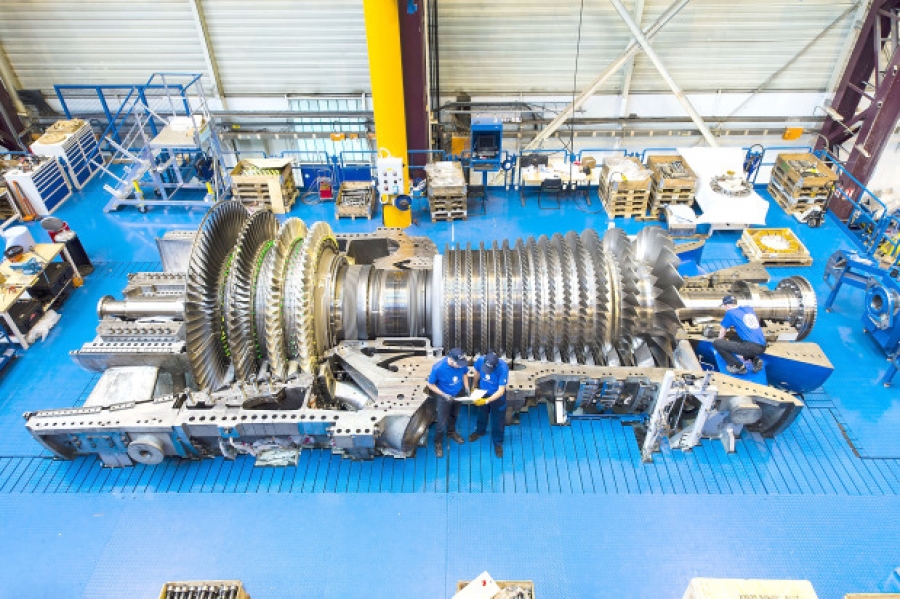
Top steam turbine manufacturers in world– Steam turbines are used to power sources that produce electricity, as well as to provide propulsion for ships, planes, and missiles, and may be found all over the world. They transfer heat energy in the form of evaporated water into motion by applying pressure to spinning blades. The steam turbine has been developed to the millimeter, and it is one of the most difficult things to design and build. Large steam turbines are produced in only a few areas around the globe. We’ve prepared a list of the top steam turbine manufacturers in the world in this post.
On the Linquip website, you will discover all the information you need about steam turbines and their related products, as well as industry-related information. We, at Linquip, are committed to providing you with as much general and reliable information about steam turbines as possible, whether you’re an industry professional or a customer. in Linquip, you will find a list of all Steam Turbine Manufacturers.
Interested in finding out how we can contribute to your industry’s revenue? With Linquip’s Solutions for Each Company Level, you will be provided with various options to upgrade the business capability of your company. We offer a variety of services, from the simplest to the most advanced marketing and advertising packages, to help you attract more customers to your business. What information would you like to find regarding the price of steam turbine devices and equipment? If you use Linquip’s platform, you will have the option of sending a request to a wide range of Steam Turbine Suppliers and Companies and receive free quotations from each of them.
Descriptions on Steam Turbine
What Is a Steam Turbine?
A Steam Turbine is a mechanism that extracts thermal energy from pressured steam and converts it to mechanical work. Because it provides rotational motion, the turbine is particularly suited to powering electrical generators. Steam turbine generators at central power plants such as solar thermal electric, nuclear, and coal power plants produce more than 88 percent of the energy in the US, according to the US Department of Energy. The fact that a steam turbine is powered by steam gives it its name. As steam passes through the turbine’s spinning blades, it expands and cools, releasing the majority of the energy it contains. Because of the steam, the blades are constantly spinning. As a result, the blades convert the vast majority of the steam’s potential energy into kinetic energy. The turbine is then used to power a generator, which produces electricity. The most basic components of a steam turbine are the blades and rotors. A group of blades is referred to as a “stage.” They have steam inlets and outputs as well.
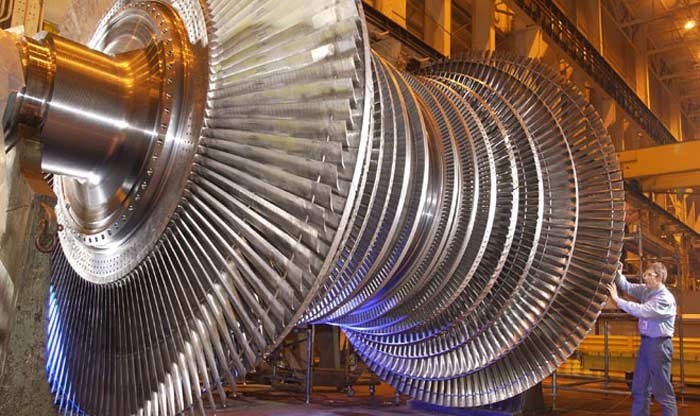

Operational and Design Principles
The entropy of the steam entering the turbine equals the entropy of the steam leaving it, making an ideal steam turbine an isentropic process. In contrast, no steam turbine is totally isentropic, with typical isentropic efficiencies ranging from 20% to 90% depending on the turbine’s use. The interior of a turbine is made up of several sets of blades or buckets. One set of stationary blades is attached to the casing, while another set of moving blades is connected to the shaft. The sets are coupled with certain minimum clearances, with the size and layout of the sets changing at each stage to maximize steam expansion.
The thermal efficiency of a steam turbine is affected by its size, load, gap losses, and friction losses. They can achieve peak efficiency of roughly 50% in a 1,200 MW (1,600,000 hp) turbine; smaller turbines have lesser efficiency. To improve turbine efficiency, steam is expanded and put to work in a series of processes. The amount of energy taken from these stages determines whether they are categorized as impulse or reaction turbines. Most steam turbines use a combination of reaction and impulse designs, with each stage operating as either one or the other, but the prevalent turbine employing both. Lower pressure stages are usually response types, while higher pressure stages are usually impulse types.
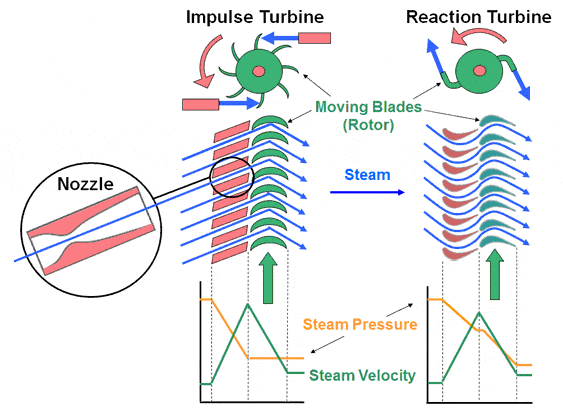
Impulse Type of Steam Turbine
Fixed nozzles direct the steam flow into high-speed jets of an impulse turbine. The bucket-shaped rotor blades transfer the kinetic energy of these jets into shaft rotation as the steam jet changes direction. The pressure loss is limited to the stationary blades, resulting in a net increase in steam velocity over the stage. As the steam flows through the nozzle, the pressure drops from the inlet to the output pressure (atmospheric pressure or, more usually, the condenser vacuum). Because of the high ratio of steam expansion, steam leaves the nozzle at a high velocity. As it leaves the nozzle, the steam leaving the rotating blades has a large fraction of its maximal velocity.
Reaction Type of Steam Turbine
The reaction turbine’s rotor blades form convergent nozzles when they are aligned. In this sort of turbine, the reaction force created when the steam accelerates through the nozzles formed by the rotor is utilized. The stator’s fixed vanes direct steam onto the rotor. It emerges from the stator as a jet that completely fills the rotor’s diameter. In comparison to the blades, the steam then reverses direction and builds up speed. A pressure drop develops across both the stator and the rotor as steam accelerates through the stator and decelerates through the rotor, with no net change in steam velocity across the stage but a reduction in both pressure and temperature, representing the work generated in the rotor drive.
Types of Steam Turbine
A steam turbine is a large turbo machine that generates mechanical energy from thermal energy. All steam turbines can be classified into several categories based on the number of general flow, cylinders, heat source, working principle, and flow direction. They can also be classified according to exhaust conditions, casting or shaft design, and drive type. However, there are two sorts of steam turbines: impulse and reaction, as previously indicated. Condensing, non-condensing, automated extraction, mixed pressure, and regenerative extraction are the five fundamental types of steam turbines based on exhaust circumstances.
A) Types Based On Principle of Operation:
- Impulse turbine
- Reaction turbine
B) Types Based On Number of Cylinders:
- Single Cylinder Turbine
- Multi-Cylinder Turbines
C) Types Based On Direction of Steam Flow
- Axial Flow Turbine
- Radial Flow Turbine
- Tangential Flow Turbine
D) Types Based On Means of Heat Supply
- Single Pressure Turbine
- Reheat Turbines
- Dual Pressure Turbine
E) Types Based On Exhaust Condition
- Condensing Turbine
- Non Condensing Turbine
Operation and Maintenance
After first rotating the turbine with the turning gear, providing time for the rotor to acquire a straight plane (no bowing), the turning gear is released and steam is admitted to the turbine, first to the astern blades, then to the ahead blades, slowly revolving the turbine at 10–15 RPM (0.17–0.25 Hz) to slowly warm the turbine. Warm-up times for large steam turbines can take up to 10 hours.
Due to the high rotation velocities, rotor imbalance might cause vibration, which could result in a blade breaking away from the rotor and passing through the casing. To reduce this risk, a lot of effort is put into balancing the turbine. High-quality steam, either superheated (dry) or saturated with a high dryness fraction, is also used to power turbines. This shields the blades from being bombarded with condensed water, which causes impingement and deterioration quickly (moisture carry over). The thrust bearings on the turbine shaft may be damaged by liquid water entering the blades. To prevent this, condensate drains are installed in the steam pipework leading to the turbine, as well as controls and baffles in the boilers to ensure high-quality steam.
Top Steam Turbine Manufacturer in the World in 2023
The table below shows the top Steam Turbine Manufacturers in the World, along with their annual sales. Following is more information on each company’s headquarters location, as well as the number of employees and descriptions of corporate operations.
Table 1: Top Steam Turbine Manufacturer in the World in 2023
| Company | Headquarters | No. of Employees | Annual Sales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bradken, Inc. (Engineered Products Business) | Kansas City, MO | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America, Inc. | New York, NY | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| Turboatom | Kharkov, Ukraine | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) | Delhi, India | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| TURBOPAR Group | Smolensk, Russia | 100-200 | NA |
| Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Europe, Ltd. | Duisburg, Germany | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| Siemens Energy | Munich, Germany | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| General Electric Co. | Boston, MA | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| Dongfang Electric Corp Ltd | Sichuan, China | 1000+ | $250 Mil. and over |
| Sande Stahlguss GmbH | Sande, Germany | 200-499 | NA |
Top Steam Turbine Manufacturer in the World in 2023 Summaries
Top 10 Steam Turbine Manufacturers in World include:
- Bradken, Inc. (Engineered Products Business)
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America, Inc.
- Turboatom
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
- TURBOPAR Group
- Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Europe, Ltd.
- Siemens Energy
- General Electric Co.
- Dongfang Electric Corp Ltd.
- Sande Stahlguss GmbH
Bradken, Inc. (Engineered Products Business)
Bradken is a metal casting and foundry firm based in the United States that specializes in custom-designed iron and steel parts and equipment. The world’s largest mining businesses rely on this company for customized products such as ground engaging tools (GET), crawler shoes, mill liners, crusher liners, wear solutions, and monitoring systems. In addition, they provide specialist structural and industrial casting services in a variety of alloys, with casting capacities ranging from 500 grams to more than 25 tons. Bradken has sales and service teams all around the world, as well as foundries and workshops. They employ approximately 3,000 people in 20 production facilities and 40 sales and service centers across Australia, the United States, India, Indonesia, New Zealand, Canada, Malaysia, South Africa, China, and South America. They also manufacture custom turbines, including steam turbines. Steam turbines are used in a variety of applications, including process equipment, power generation, hydro, military, mining, construction and industrial machinery, shipbuilding, and transportation.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America, Inc.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America, Inc. supports aircraft and aerospace projects, including the MU-2 and MU-300, at their long-time approved Mitsubishi Service Center, Intercontinental Jet Service Corp. in Tulsa, Oklahoma. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America Corrugating Machinery Division also provides knowledgeable equipment systems, sales, parts, technical, and field support to the developing, dynamic packaging industry, making it one of the most respected converter providers in North and Central America. Their patented post-combustion capture technologies allow industrial and power plants to absorb and retain up to 90% of CO2 emissions, putting them at the forefront of green technology adoption. It is how they make a positive difference in the world.
Since 1991, the Tire Machinery Division of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America, Inc. (MHIA) has been manufacturing and assembling tire industry equipment in Northeast Ohio. MHIA works with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (Japan) and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Machinery Technology Corporation to provide world-class designs, engineering, and equipment to the tire industry. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America, Inc.’s Transportation Systems Division is in charge of the design, development, supply, engineering, marketing, and installation of innovative transit systems for the global market. In addition to their world-class Automated People Mover (APM) systems, they have a diverse product portfolio that includes rail transit, maglev, monorail, and short-haul transportation systems that can all be customized for practically any application.
Turboatom
Turboatom is one of the world’s largest manufacturers of steam turbines for thermal power plants (TPP), central heating plants (CHP), and nuclear power plants (NPP); hydro turbines for hydro power plants (HPP) and pumped storage power plants (PSPP); and hydro valves for HPP, PSPP, and pumping plants. Production capacity of Turboatom allows for the production of steam and hydro turbines with total intended capabilities of 8 million kW and 2 million kW per year, respectively. The turbine is manufactured in a closed cycle, beginning with development and research and ending with manufacturing, assembly, testing and shipping.
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
The Heavy Electrical Equipment industry in India began with the establishment of BHEL in 1956. In 1974, Heavy Electricals (India) Limited joined with BHEL. BHEL was founded in 1956 as a simple manufacturing PSU with Soviet Union technological assistance. It was at the forefront of thyristor technology in the 1980s. BHEL became a publicly traded corporation in 1991. It eventually established the ability to manufacture a wide range of electrical, electronic, and mechanical equipment for various industries, including transmission, transportation, oil and gas, and associated industries. The sale of power production equipment such as turbines and boilers, however, still accounts for the majority of the company’s revenue. BHEL-supplied equipment accounted for almost 55% of India’s total installed power production capacity as of 2017. The company also provides electric locomotives to Indian Railways and defense equipment to the Indian Armed Forces, including the Super Rapid Gun Mount (SRGM) naval weapons and simulators, which are produced in collaboration with the Ordnance Factory Board.
TURBOPAR Group
Energotrade LLC owns the registered trademarks TURBOPAR and TURBOPAR Group of Companies (Russia). The partnership includes enterprises from Russia, Kazakhstan, and Belarus, as well as a design institute and a steam turbine manufacturing plant. The TURBOPAR group of companies is made up of companies that are involved in the following activities:
- Supply of Italian steam boilers, industrial steam generators, hot water boilers, and industrial autoclaves;
- Manufacturing of boiler house chemical water treatment equipment;
- Manufacturing of steam turbines;
- Installation and adjustment of boiler rooms, as well as installation and adjustment of steam turbines;
- Construction of block-modular boiler houses, as well as the manufacture of boiler house chimneys;
- Production of wet cooling towers.
Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Europe, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Power in Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) is a prominent provider of innovative technology and solutions for the energy sector. They employ over 1,000 people in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. In the region, they have centers of excellence in Germany, the United Kingdom, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. They also offer customer service skills in nations throughout the area.
In an increasingly regulated industry, the greatest problem facing the electricity sector today is guaranteeing reliable power generation and delivery while lowering CO2 emissions. Mitsubishi Power, as a trusted partner and a pioneer in innovative technology and solutions, is effectively facilitating this energy transition for their clients.
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy AG is a leading energy technology company in the globe. The company collaborates with customers and partners on future energy systems, assisting in the transition to a more sustainable world. Siemens Energy’s product, solution, and service portfolio spans nearly the whole energy value chain, from power generation to transmission and storage. The portfolio includes traditional and renewable energy technology, such as gas and steam turbines, hydrogen-fueled hybrid power plants, and generators and transformers. More than half of the portfolio has been decarbonized already. Siemens Energy is the global market leader for renewable energies thanks to a majority ownership in Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy (SGRE), a publicly traded corporation. Siemens Energy technologies are responsible for approximately one-sixth of all electricity generated worldwide. In fiscal year 2019, Siemens Energy employed 91,000 employees in over 90 countries and produced sales of roughly €29 billion.
General Electric Co.
GE is a multinational conglomerate headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts, that was formed in New York State. The company operated in several industries until 2021, including aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, locomotives, weapons manufacturing, and venture capital and finance, but it has since divested from several of them, with the first four segments now accounting for the majority of the company’s operations.
On November 9, 2021, the corporation declared its intention to separate into three public organizations. The new companies will focus on healthcare, aviation, and energy (renewable energy, power, and digital). The healthcare division’s initial spinoff is scheduled for 2023, and the energy division’s is set for 2024.
Dongfang Electric Corp Ltd.
Dongfang Electric Corporation (DEC) is one of the critical enterprise groups controlled directly by the Chinese Central Government. DEC has grown into one of the world’s major power generating equipment manufacturers and international project contractors, with its headquarters in Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan Province, which is known as the “Hometown of Giant Panda” and the “Heavenly Land on Earth” and the Currently, DEC’s cumulative output capacity exceeds 500GW, with annual output leading the globe for 14 consecutive years.
DEC has grown into a comprehensive organization specializing in power equipment production, cutting-edge technological R&D, international engineering projects, exporting full plants and equipment, and international economic and technical collaboration throughout the course of more than 60 years. DEC represents the top technological and manufacturing level for China’s heavy machinery and equipment industry, and it has been designated by the Chinese Central Government as one of the most important state-owned enterprise groups in terms of the national economy due to its distinguished capacity and contribution.
Sande Stahlguss GmbH
Sande Stahlguss manufactures high-quality steel castings up to 45 tons in weight. Individual pieces and small series are the focus of their work. They provide cutting-edge components for steam, gas turbines, and compressors (85%), as well as machinery, shipbuilding, and other industries (15%). Sande Stahlguss’s 200 highly qualified staff produce approximately 3,500 tons of steel components per year using two electric arc furnaces and a 30 ton AOD Converter. They have been able to satisfy our customers all over the world thanks to a sophisticated casting simulation tool, their own pattern shop, and a high-tech machining shop.
Download Top Steam Turbine Manufacturers in World PDF
There is an option to download this article in the form of a PDF file if you prefer to read it that way. You can do so by clicking on the link provided below.
Conclusion
This article has compiled data and company descriptions for some of the most well-known steam turbine manufacturers in the world, as well as a quick primer on steam turbine fundamentals. Visit the Linquip website to learn more about these companies and to identify suppliers of additional industrial and commercial equipment.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Provider
Read More In Linquip
- How Does a Steam Turbine Work? A Simple Descriptive Guide
- Types of Steam Turbine: An easy-to-understand and practical Classification
- Steam Turbine Parts: A Comprehensive and understandable Introduction to All Components
- Steam Turbine Efficiency: Complete Explanation
- Top 15 Gas Turbine Manufacturers In India
- Top Wind Turbine Manufacturers in USA (Comprehensive Guide)
- Top Wind Turbine Manufacturers In India (Comprehensive Guide)
- What is Mixed Flow Turbine? Basics, Advantages, and Applications
- What is Low Head Turbines?
- What is Kaplan Turbine? Diagram and Working Principles
- Pelton Wheel | Parts, Types, Working Principle and Efficiency



