
Piston Valve? Working Principle & Function
A Piston Valve is a device that controls the flow of fluid via a tube or pipe by using the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder. Most of the time, these valves are utilized with fluids that produce a lot of seat wear. The majority of piston valves are manually operated, but alternative actuation modes, such as hydraulic and electronic, are used on occasion. The cost is dependent on the severity of the damage, and it's nearly impossible to estimate without physically removing the pieces and determining which ones need to be replaced. Replacing a valve is more complicated than simply removing and replacing it since the valve seat and valve guide may need to be repaired. You'll need to take the valve seat to a machining facility if it has to be restored.
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteTop Companies in Piston valve
+4 Companies in Piston valve
Top Devices in Piston valve

Emerson company

Emerson company

Emerson company
Related RFQs
piston valve
LNQ-23111089

What is a Piston valve?
Piston valves are utilized as shut-off and regulating mechanisms in hot water and steam systems. They're mostly available in globe-style body combinations.
Function of a Piston Valve
Piston valves control the flow of fluid through a tube or pipe by using the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder. Piston valves are used to regulate the on/off of steam, gas, and other fluid services by being fully open or fully closed. The majority of the time, these valves are used on fluids that cause significant seat wear. The majority of piston valves are operated manually, but other actuation modes, such as hydraulic and electric, are occasionally utilized. Piston valves are used commonly in situations where the valve body is permanently placed and maintenance is required. Piston valves are not intended for throttling and must be utilized in either completely open or fully closed states. Only the bottom face of the piston is exposed to the fluid when the valve is fully opened, while the rest of the body is shielded by the top sealing rings. As a result, the fluid movement protects the sealing surfaces from erosion.
Working Principle of a Piston Valve
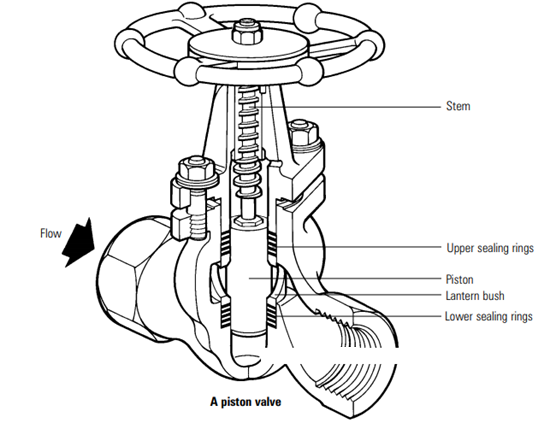
A piston valve has a similar design to a globe valve and is used to shut off and regulate fluids. These valves provide positive shutoff. The metal piston, two robust valve rings, and a metal lantern bush make up the shutoff assembly. The sealing surface comprises the piston's outer vertical surface and the sealing rings' equivalent inner surfaces. When opposed to traditional globe valves, this provides a sealing surface. A displacement at the start of the opening reveals the little flow segment, which regulates the low flow rate.
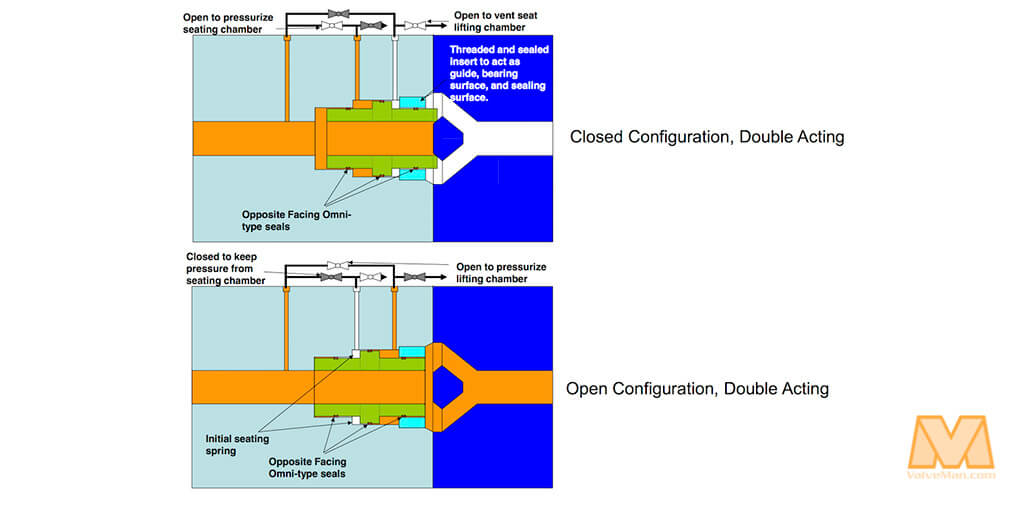
With the double-disc design, pressure can be equalized across the disc, and it can be modified to alter flow characteristics through the valve or to adjust its operation, such as by decreasing the valve's response time. The force exerted over the sitting surface is as equal as feasible while being directed in the opposite direction with a piston balance valve. The flow of the double-disc configuration is from the left. The fluid pressure would press against the bottom of the top disc and the top of the bottom disc in the closed position, equalizing flow pressure. Even when the valve is open, there is an equalizing force at work, allowing the valve to operate smoothly.
Parts of a Piston Valve
Piston valve parts include:
- Body
- Piston
- Bonnet
- Lantern bush
- Valve rings
- Gland
- Spindle
- Handwheel
- Packing
- Bonnet stud
- Yoke bush
- Gland eyebolt
The classic seat and cone are replaced with a piston and lantern bush in piston valves, which are a variation of the traditional globe valve. The piston is made of chrome steel that has been meticulously machined, and the sealing rings are frequently made of self-lubricating Teflon. The cast usually constructs the body, which may have screwed ends, flanged ends, or butt welding ends. The bonnet is also made of the same material as the body and is bolted together.
A piston seals the system properly with the help of two tough seats. The piston is attached to the valve stem and handwheel, and it travels between two sealing rings separated by a lantern bush. The load exerted along the stem compresses the two sets of sealing rings around the piston when it is constructed. The upper set of sealing rings serves as gland packing, while the bottom set serves as a seat. The huge sealing surface between the piston and rings ensures high-level shut-off tightness.
All of the internals of the valve can be simply removed by releasing the cover nuts and withdrawing the piston if it needs to be serviced. An extractor tool can be used to remove the rings and the lantern bush. This procedure can be carried out without having to remove the valve from the pipeline. Piston valves have a long service life, however, the sealing ring may wear out after a lengthy period of operation.
You can find a great deal of Piston Valve Companies and Manufacturers in Linquip, along with expert Service Providers.
Types of Piston Valves
The two types of piston valves are balanced and unbalanced. In high-pressure applications, balanced valves are employed, while in low-pressure applications, unbalanced valves are used. The type and the normal are the two sorts of piston designs that are accessible. The bottom half of the piston in the regulating type is tapered to create a throttling effect. The heart of a piston valve is the sealing ring.
Applications of Piston Valves
Piston valves are generally utilized in power plants, refineries, pulp and paper mills, and other similar facilities for saturated and superheated steam and hot water distribution. A few examples are steam headers and manifolds, condensate, desuperheaters, steam trap isolation, and other uses. They come in sizes ranging from 1/2 to 8 inches in ANSI class 150, 300, and 800. For face-to-face and flange dimensions relevant to globe-type pipeline valves, many, if not all, piston valves will be designed according to DIN standards or ANSI and ASME specifications. The lower series valves will typically be made of cast steel, whereas the higher series valves will be made of forged steel. Depending on the class, ends may be flanged, threaded, butted, or socketed.
Gases such as oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen can also be handled using piston valves. Heat transfer oils and different chemicals are also used with them.
Piston valves are also used as a tank and reactor drain valves, with the piston, referred to as a ram. Because the piston and seal combination is self-cleaning, these valves may drain tanks containing slurries or even powders. Unlike the globe-style piston valve, the ram-style piston valve is normally wye-shaped to lessen fluid flow restriction. In addition, the ram carries a second seal with it on its journey.
Piston valves are superior to globe valves at tolerating dirt in the lines while still sealing properly. The valve port remains closed until the piston has entirely withdrawn from the seal ring after it has been opened, minimizing any corrosion on the sealing surfaces caused by flowing fluid. The seals are suited for modulating applications because they can withstand partial opening without eroding. In some cases, a needle-shaped extension can be placed to the front of the piston to improve flow control. The seals wash away any particles that have accumulated on the piston as the valve is closed. Piston valves can continue to function efficiently even if they have been installed but not utilized for a long time.
Linquip offers a wide variety of Distributors, Experts, and Equipment for Sale of Piston Valves.
FAQs about Piston Valves
- Why is a piston valve used for steam?
One type of valve used to control the flow of steam within a steam engine or locomotive is the piston valve. They regulate the flow of steam into the cylinders and the subsequent exhausting of steam, allowing a locomotive to operate on its own.
- What is the role of a piston valve in a water pump?
The upstroke of the piston of a lift pump pushes water into the bottom half of the cylinder through a valve. Water flows into the top half of the cylinder through valves in the piston on the downstroke. Water is ejected from the upper half of the cylinder via a spout on the following upstroke.
- How many types of piston valves are there?
There are two types of piston valves: balanced and unbalanced. A balanced valve is utilized in high-pressure applications, while an unbalanced valve is used in low-pressure applications.













