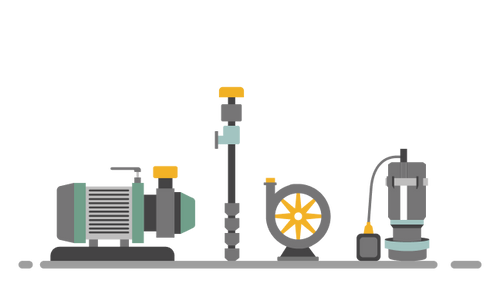
Pump: Working Principles, Function & Diagram
There are different types of pumps and, mainly depend on your requirements and application, one of them are best for you. Your application mainly define what type of fluid you want to move, the distance you need to move the fluid, and the amount of fluid you want to transfer per a particular time frame. However, other parameters like cost of purchase and cost of maintenance are also important and all these parameters could make it complicated to decide which kind of pump to use for your application. At Linquip, our goal is to help you select and purchase the best pump possible for your application, and we are here to help you on all stages of design, purchase, and maintenance. Feel free to browse our comprehensive list of pumps, pump manufacturers, and service providers in different categories, or if you feel overwhelmed, just contact us and our experts will help you on with every stage of your project.
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuotePump Subcategories

Top Companies in Pump
+1054 Companies in Pump
Top Devices in Pump
Related RFQs
Dry Vacuum Pumps
LNQ-24011129
Centrifugal Pumps category
LNQ-23121064
Pump category
LNQ-23121024
overhung centrifugal pump
LNQ-23121021
RECIPROCATING PLUNGER PUMP
LNQ-23101197
Centrifugal Pumps category
LNQ-23101107
vane pumps
LNQ-23101105
End suction pump
LNQ-23101104
Top Pump Experts

What Is Industrial Pump?
A pump is a machine that circulates fluid within a system by forcing it to move. Using mechanical action, a pump moves liquids. Industrial pumps are used in several industries, such as agriculture, petroleum, automotive, and construction. The information in this article will help you understand how pumps function as well as how they are used.
We have provided a complete list of the Industrial Pump for Sale in Linquip. Also, a list of Pump Suppliers and Companies as well as Pump Manufacturing can be found in Linquip.
Working Principle of Industrial Pump
Various types of pumps function on different principles to move the fluid. Usually, pumps operate by reciprocating or rotating mechanisms as well as using energy for mechanical work to move fluid through different parts. The use of these mechanisms in industrial pumps is gaining popularity as each of them has benefits for the pumping process.
Reciprocating
Repeatedly going up and down or going back and forth is reciprocation. A wide range of mechanisms employs it, including reciprocating engines and pumps. A reciprocation cycle consists of two opposite motions called strokes.
Rotary
Rotary pumps move fluid using rotating mechanisms that create a vacuum that draws in and captures the liquid.
Function of Industrial Pump
Industrial pumps are devices that move liquids between two locations. As their names suggest, these pumps are used in the industrial context. They can be used to pump water from wells, filter aquariums or ponds, cool and inject fuel in vehicles, operate cooling towers, or pump oil and gas.
The use of an industrial water pump is beneficial no matter what type of fluid you are processing, be it oil, water, industrial chemicals, or wastewater. You can use these pumps to move and accelerate the fluids when they are required to move at high rates. A mechanical pump would be an example of this type of pump.
Understanding the operating basics of industrial pumps requires some considerations based on the type of pump used. Here is a brief discussion:
Power Source
As a general rule, the pump can be powered by manpower, electricity, or even wind power. Depending on their size, these energy sources can range from a micro microscope for medical use to industrial pumps for water supply systems or industrial pumps for transferring coolant in types of machinery. Pumps of this type must be resistant to corrosion during the pumping process.
Impeller Number
Impellers are rotors used to increase the flow and pressure of a fluid. The number of impellers determines the pump's operating mode and its ability to deliver liquids. A pump with only one revolving impeller is known as a single-stage pump. Pumps that contain more than one revolving impeller are referred to as double-stage pumps or multistage pumps.
Chemical and biomechanical pumps have been developed for many different applications in the biological field. Some mechanical pumps are designed by using biomimicry. As in the old days, people studied birds for the purpose of making humans fly. Even though such efforts are not always successful, there are many biological imitation cases that contribute to improving scientific research.
Positive Displacement
In a positive displacement pump, a fixed quantity of liquid is drawn and forced down into a discharge pipe in order for it to flow. In general, positive displacement pumps have an expanding cavity on the suction side and a decreasing cavity on the discharge side. As the suction side cavity expands, the liquid flows into the pump, and as the cavity contracts, the liquid flows out of the discharge port. The volume of the liquid remains constant during each cycle.
The flow rate remains the same with positive displacement pumps regardless of the output pressure, unlike centrifugal pumps. So, the positive displacement pump falls into the category of constant flow pump equipment.
As the pressure increases, however, the internal leakage will also increase slightly, resulting in a flow that is not truly constant. Therefore, the positive displacement pump cannot work against the closed valve on the discharge side because it lacks a closing valve similar to that of a centrifugal pump. After that, the closed discharge valve, the positive displacement pump, continues to produce flow, and the pressure in the discharge line continues to rise until the line bursts, causing severe damage to the pump.
Pump Curve
You do not want your pump to operate below its standard curve. In order for your pump to operate at its normal curve, which corresponds to the speed and flow, preventive measures are required. An expert will need to compare the pump's flow and other variables to its standard curve.
Linquip provides a wide selection of Pump Industry Experts.
Usage of Industrial Pumps

Our lives cannot be complete without pumps, which are common household and industrial facilities. As a result of market demand, industrial water pumps have changed from simple mechanical systems to intelligent fluid mechanics equipment. The future pump structure will integrate sensors, transmissions, small CPUs, and other information technology to achieve the goal of intelligent manufacturing for the entire production process.
There are a wide variety of applications across industries, including:
- Agriculture. Animals can be hydrated, irrigation can be facilitated, slurries can be moved, pressure washing for animal stalls can be done, and many other uses can be found for pumps in the agricultural sector.
- Industrial. Pumps serve a variety of purposes in the industrial sector, including transporting process chemicals, supporting manufacturing processes, boosting pressure, filtration, and numerous other functions.
- Construction. Various pumps are used in construction to reduce flooding risk, maintain construction sites, and supply pressurized water for cleaning.
- Engines. Gas engines rely on internal pumps to move fuel for combustion.
- Fire suppression. Fire suppression systems require pumps to keep pressurized water flowing. Pumps are also used by fire trucks to draw water via hydrants in the municipal system.
- Flood prevention. In commercial and industrial buildings, sump pumps and other submersible pumps prevent flooding.
- Municipal. The maintenance of water pressure within municipal water networks is made possible by an equally complex system of pumps.
- Sewage and waste. The movement of various liquid and solid wastes is facilitated by pumps.
Common Applications of Industrial Pumps
Industrial pumping offers a wide range of services, including:
- Pumping from wells
- Aquarium filtration tasks
- Pond filtration works
- Water cooling
- Fuel injection for the automotive industry
- Oil and gas operations for the energy sector
- Moving of fluids and coolants using industrial pumps in the field of machine tools
- Biochemical processes with the use of industrial pumps to develop and manufacture drugs
- Artificial replacements for human body parts, including artificial hearts and penile prostheses.
FAQ about Industrial Pump
- What Is an Industrial Pump?
Industrial pumps are usually heavy-duty pumps used to move many different types of materials, including water, chemicals, petroleum, wastewater, oil, sludge, slurry, or even food. The most common types of pumps used in industrial settings are centrifugal pumps and positive displacement pumps.
- Which Pump Is More Efficient?
When different pump designs are available, centrifugal pumps are generally the most cost-effective, followed by rotary and reciprocating pumps. Despite the higher efficiency of positive displacement pumps, the added costs of maintenance tend to counteract this advantage.